24 Jul Marshallian Approach
Marshallian Approach to Price Determination – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Introduction
The determination of prices is a central theme in microeconomics. Among the many theories explaining this process, the Marshallian approach, developed by British economist Alfred Marshall, remains foundational. His framework emphasizes the interaction of demand and supply within a partial equilibrium framework. Understanding this approach is essential for aspirants of the UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE) who have chosen Economics as their optional subject.
1. Background of the Marshallian Approach
Alfred Marshall’s seminal work, “Principles of Economics” (1890), laid the foundation for the modern microeconomic theory. He emphasized that both demand and supply should be considered simultaneously to understand price formation. Unlike the classical economists who focused only on supply-side factors (like cost of production), Marshall gave equal importance to the consumer side — demand.

Marshall’s Equilibrium Graph
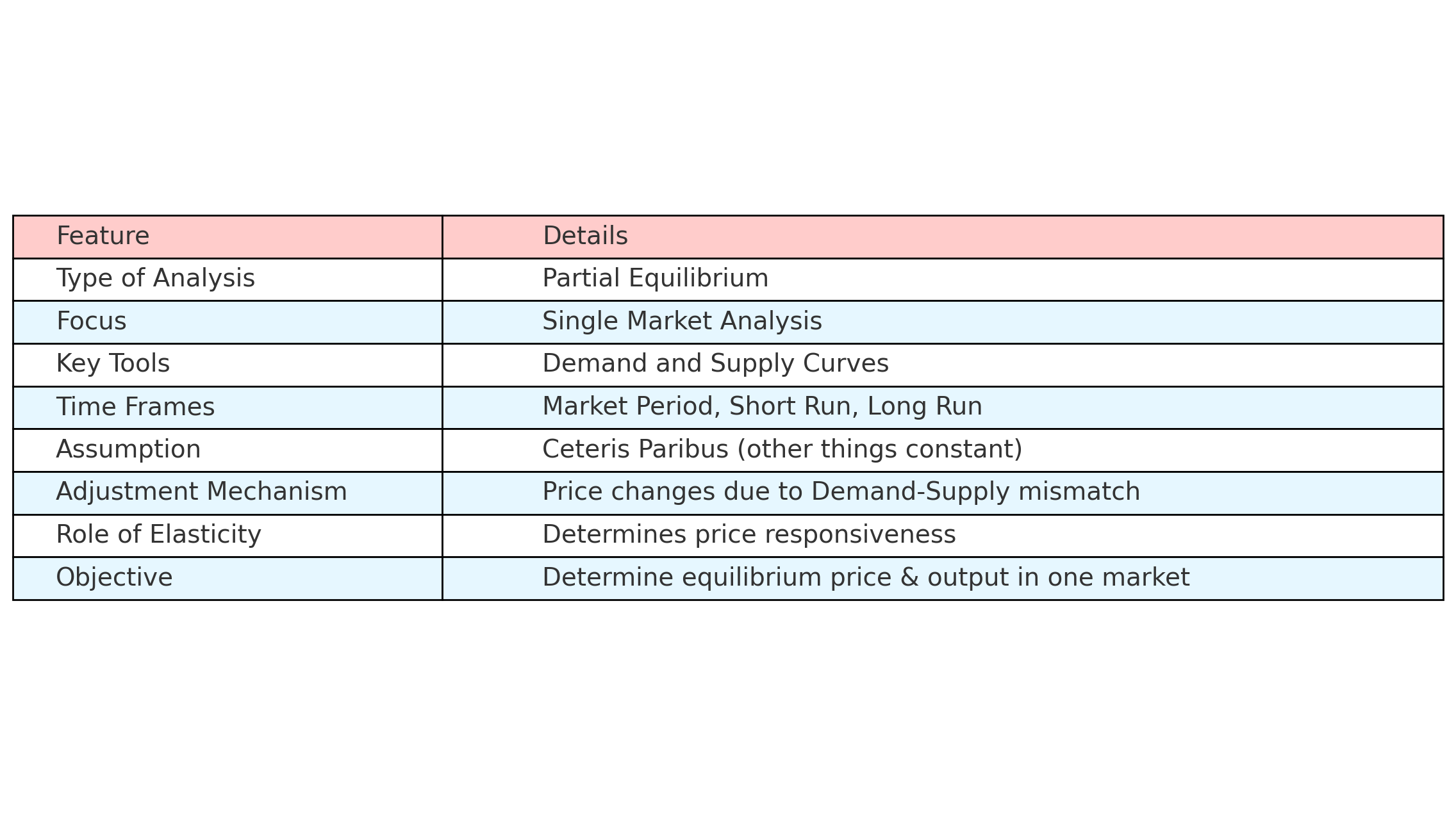
2. Key Features of the Marshallian Approach
- Partial Equilibrium Analysis: Focuses on a single market, assuming other factors remain constant (ceteris paribus).
- Demand and Supply Curves: Graphically represent consumer willingness to buy and producer willingness to sell at different price levels.
- Equilibrium Price: Determined at the point of intersection between demand and supply curves.
- Time Element: Introduced different time periods for price adjustment (Market, Short Run, and Long Run).
- Elasticity: Price elasticity of demand and supply play a crucial role in how prices adjust in response to shifts.
3. Time Element in Price Determination
Marshall’s innovation was his introduction of the time element in price determination:
- Market Period: Supply is fixed (e.g., perishable goods). Price is solely determined by demand.
- Short Run: Firms can change some inputs (like labor), but not all. Price is determined by both demand and supply.
- Long Run: All factors are variable. New firms can enter or exit, and prices reflect long-run equilibrium.
This framework allows for more realistic predictions of price behavior in different timeframes.
4. Price Determination Mechanism
The Marshallian approach uses a graphical model:
- Price is determined where the demand curve intersects the supply curve.
- When demand increases (rightward shift), the equilibrium price and quantity rise.
- When supply increases (rightward shift), the equilibrium price falls, and quantity rises.
It provides a static analysis in a given time period, assuming all other markets remain unchanged.
5. Role of Elasticity in Price Adjustment
Marshall emphasized the importance of elasticity in determining the effect of demand or supply changes:
- Elastic Demand: A shift in supply leads to smaller changes in price and larger changes in quantity.
- Inelastic Demand: The same shift causes significant price changes.
- Elasticity of supply also determines how easily producers can adjust to price changes.
6. Ceteris Paribus Assumption
The approach assumes all other factors remain constant. For example:
- Consumer income remains unchanged
- No change in technology
- No external shocks
While simplifying analysis, it limits real-world applicability, especially in dynamic markets.
7. Strengths of Marshallian Approach
- Simple and intuitive for single-market analysis.
- Incorporates both demand and supply in price theory.
- Helps understand short-run and long-run price behavior.
- Foundation for applied microeconomics and welfare economics.
8. Limitations of Marshallian Approach
- Ignores interdependence of markets (solved later by Walrasian model).
- Assumes static environment (no dynamic feedbacks).
- Not suitable for complex macroeconomic modeling.
9. Infographic
best economics optional test series
10. Mind Map

Marshallian Approach MindMap
11. Previous Year UPSC Economics Optional Questions
- UPSC 2023: Explain the significance of time element in Marshallian price determination.
- UPSC 2020: How do demand and supply interact in Marshall’s price theory?
- UPSC 2018: Discuss the role of elasticity in determining the equilibrium price.
12. Probable Questions for UPSC Prelims & Mains 2025
- Mains: Discuss the significance of time element in Marshallian theory of price determination.
- Mains: “Price is determined by both blades of a scissor.” Discuss with reference to Marshall.
- Prelims: The market period in Marshall’s theory implies:
- Prelims: Which of the following best defines partial equilibrium?
13. Conclusion
The Marshallian approach offers a robust and foundational understanding of how prices are determined in individual markets. While it has limitations in terms of real-world applicability and inter-market dynamics, its conceptual clarity and simplicity make it a powerful analytical tool. For UPSC aspirants, especially with Economics optional, mastering this approach not only helps in tackling direct questions but also strengthens their microeconomic base.




No Comments