05 Oct MGNREGS to fund work to reverse desertification of land across States
LAND DEGRADATION
The topic is based on how Land Degradation impacts India’s Bio-diversity & climate change.
CONTEXT
India has been facing the problem of Land Degradation and desertification persistently. To reverse these, a huge amount of investment is needed. But with limited funds, this seems like a distant dream. To tide over this difficulty, the government is planning to bring convergence between the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) and the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY)
WHAT IS LAND DEGRADATION
- It is the deterioration or loss of the productive capacity of the soils for the present and future.
- It leads to various threats like food insecurity, higher food prices, climate change, environmental hazards, and the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services
- It can happen in various ways like soil erosion, acidification, desertification, salinization, etc.
- It is happening at an alarming pace and currently, about 25% of global land is degraded.
- According to the Desertification Atlas published by the Environment Ministry in 2021, at least 30% of India’s total geographical area is under the category of “degraded land”
- The most glaring example of soil degradation is seen in the states of Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Delhi, Gujarat, and Goa which have more than 50% of their land area undergoing desertification or degradation.
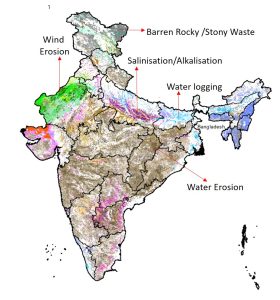
Pic: LAND DEGRADATION
REASONS For LAND DEGRADATION
- Deforestation: Forests play a vital role in maintaining soil health. Tree roots bind soil particles preventing easy erosion. Urbanization creates more pressure on land and forests are cut down to build houses and supply timber. This contributes to the reduction of land in a significant manner.
- Overgrazing: India has a large livestock population. While it contributes to farmers’ income, it has led to the overexploitation of pastures. The lack of vegetation cover leads to soil erosion.
- Fertilizer overuse: Overuse of fertilizers and pesticides adversely affects soil quality. Nutrients are depleted this way.
- Salinization: Salinisation is the increasing salt content within the soils. India has approximately six million hectares of saline land.
- Soil erosion: Soil erosion refers to the removal of the top fertile layer of the soil. Wind and water are the main agents of soil erosion. In the absence of tree cover, strong winds blow away the loose soil particles to great a distance. Heavy rains or running water may lead to the removal of the top layer of soil. This leads to sheet erosion
- Climate Change: It may increase desertification through alteration of spatial and temporal patterns in temperature, rainfall, solar radiation, and winds.
- Non-adoption of soil conservation measures: Non-adoption of soil conservation measures like crop rotation, contour plowing, mulching, terrace farming, etc further aggravates the problem of soil degradation.
IMPACT OF LAND DEGRADATION
- It leads to loss of soil productivity: It leads to loss of soil and agricultural productivity. This poses a threat to food security and the livelihood of farmers.
- Water Scarcity: It has an adverse effect on water. It leads to an increased us to compensate for the degraded soil causing depletion of water both on the surface and in the groundwater table.
- Increased GHGs emissions: It leads to higher emissions of GHGs and in turn, increases their concentration in the atmosphere.
- Loss of biodiversity: Between 1970 and 2012 the average populations of wild land-based species fell by 38 %, and freshwater species by 81 %.
LINKING OF PRADHAN MANTRI KRISHI SINCHAI YOJNA AND MGNREGS
- PMKSY is a significant scheme to reduce soil degradation.
- The Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP) under PMKSY helps water to reach a larger distance and cover more area.
- The Watershed development program under PMKSY helps in the proper management of runoff water and improves soil conservation. This is done by using techniques like rainwater harvesting, drainage line treatment, in situ soil moisture conservation, etc
- The Central Government has recommended states carry out the components of PMKSY using MGNREGS funds
- The MGNREGA scheme has a budget of ₹73,000 crores for the year 2022-2023, By using this for PMKSY, the government can increase the area to be covered.
- By the Ministry’s estimate, convergence with the MGNREGS could help take up treatment of about 30% more land than feasible with the current scheme size.
- During COP 14 of the UN Convention to Combat Desertification(UNCCD), India put forward an ambitious target of restoring 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030. If the above schemes work in tandem, India can follow the path toward reaching this target.
WAY AHEAD
There is a need to take further steps to counter land degradation. This includes the following:
- Afforestation: An afforestation drive to plant more trees should be taken up
- Planting Windbreaks: This checks on soil erosion by wind. It checks wind movement and conserves soil.
- Controlling overgrazing: This leads to the removal of grass from roots and leads to erosion of soil. Separate ground for pastures should be created and fodder should be made available.
- Controlling mining: Mining contributes a big time to land degradation. This problem is aggravated by illegal mining which does not follow any pollution control protocols. Cleaner techniques need to be adapted to check it.
- Adoption of Soil Conservation Management Practices: Terrace farming, rainwater harvesting, contour bunding, etc are easy methods and go a long way to preserving soil
SOURCES:
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Looking for Daily Current Affairs for UPSC examination for enhancing your General Knowledge. Plutus IAS provides daily important current affairs for UPSC, IAS, SSC, and other competitive examinations. In the present era, Reading only current affairs is crucial for any IAS aspirant to gather knowledge on national and international news. So get new current affairs from our Daily current affairs in English




No Comments