04 Mar MSME building blocks of the Indian Economy
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and topic details of MSME building blocks of the Indian Economy
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-3- Economics -MSME building blocks of the Indian Economy
FOR PRELIMS
What is the new MSME classification, and why was it changed?
FOR MAINS
Why are MSMEs important for India’s economy? What challenges do they face, and how can they be improved?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has said that the MSME sector contributes significantly to the country’s economy as a key driver of innovation and growth. He will participate in three Post-budget webinars. These webinars are being held on MSME as an Engine of Growth, Manufacturing, Exports and Nuclear Energy Missions, and Regulatory, Investment and Ease of doing business Reforms. The webinars will provide a collaborative platform for government officials, industry leaders, and trade experts to deliberate on India’s industrial, trade, and energy strategies. The discussions will focus on policy execution, investment facilitation, and technology adoption, ensuring seamless implementation of the Budget’s transformative measures. The webinars will engage private sector experts, industry representatives, and Subject matter specialists to align efforts and drive impactful implementation of Budget announcements.

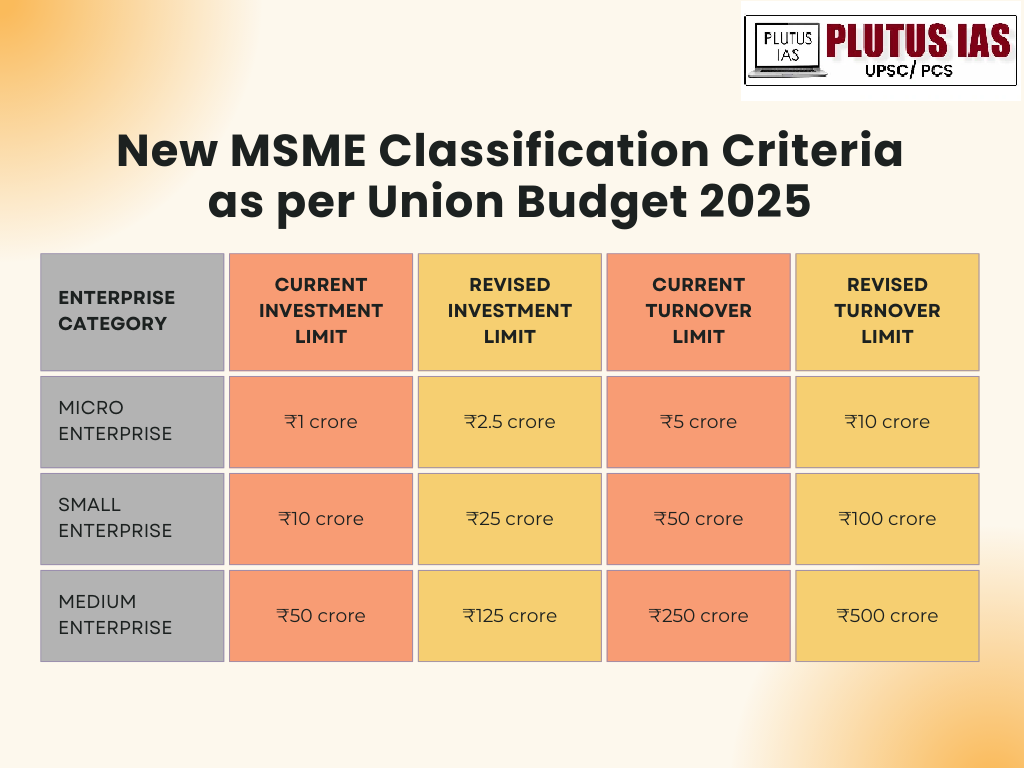
Revised definition of MSME
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a critical role in India’s economic growth, contributing significantly to GDP, exports, and job creation. Recognising their importance, the government has periodically revised the MSME classification criteria to better reflect the changing business environment and help entrepreneurs access essential benefits such as loans, subsidies, and tax incentives. In the Union Budget 2025, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a major update to the New MSME classification, increasing the investment limit by 2.5 times and doubling the turnover limits. This move is aimed at fostering growth, encouraging innovation, and creating a more enabling ecosystem for MSMEs to flourish. In this article, we will look into the new MSME definition.
| Category | Old Investment Limit | Old Turnover Limit | New Investment Limit | New Turnover Limit | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro Enterprises | Up to ₹1 crore | Up to ₹5 crore | Up to ₹2.5 crore | Up to ₹10 crore | More businesses qualify as micro-enterprises, better access to government schemes, encourages investment in technology. |
| Small Enterprises | Up to ₹10 crore | Up to ₹50 crore | Up to ₹25 crore | Up to ₹100 crore | It allows scaling up without immediate reclassification, supports expansion in production and market reach, and provides a longer growth runway. |
| Medium Enterprises | Up to ₹50 crore | Up to ₹250 crore | Up to ₹125 crore | Up to ₹500 crore | Encourages larger firms to remain in the MSME sector, enhances global competitiveness, and attracts greater investments. |
MSME Contributions in the Economy
MSME Contribution to GDP & Manufacturing GVA
| Year | MSME GVA as % of GDP | MSME Manufacturing GVA as % of All India Manufacturing GVA |
|---|---|---|
| 2019-20 | 30.48% | 40.67% |
| 2020-21 | 27.24% | 40.30% |
| 2021-22 | 29.15% | 40.83% |
MSME Share in Indian Exports
| Year | % Share of MSME Exports in Total Indian Exports |
|---|---|
| 2019-20 | 49.77% |
| 2020-21 | 49.35% |
| 2021-22 | 45.03% |
| 2022-23 | 43.59% |
| 2023-24* | 45.56% (up to September 2023) |
Key MSME Statistics: Total Employment (Udyam Registration Portal, 01.07.2020 – 06.12.2023): 15.50 crore
Estimated Credit Gap in MSME Sector (Expert Committee, RBI 2018): ₹20-25 trillion
Govt Scheme/Initiatives
1. PM Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP): Credit-linked subsidy scheme to promote self-employment.
2. Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Provides loans up to ₹10 lakh for micro and small enterprises.
3. Credit Guarantee Scheme: Facilitates collateral-free loans up to ₹5 crore for MSMEs.
4. Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund: ₹50,000 crore equity infusion to support MSME growth.
5. Udyam Assist Platform (Launched on 11.01.2023): Helps formalize Informal Micro Enterprises (IMEs) for priority sector lending benefits.
6. Retail & Wholesale Traders as MSMEs (Since 02.07.2021): Enables them to avail priority sector lending benefits.
7. Non-Tax Benefits Extension: MSMEs continue to receive non-tax benefits for 3 years after an upward classification.
8. Trade Receivable Discounting System (TReDS): A digital platform for financing MSME trade receivables.
9. Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS): ₹5 lakh crore financial support for MSMEs during COVID-19 (valid till 31.03.2023).
MSME Significance
1. Employment: MSMEs are a major source of jobs, especially in rural and economically weaker areas.
2. Economic growth: MSMEs help reduce regional imbalances and promote equitable distribution of wealth.
3. Exports: MSMEs contribute to a significant portion of India’s exports.
4. Innovation: MSMEs promote innovation and create new products and services.
5. Entrepreneurship: MSMEs promote entrepreneurship and skills upgradation.
6. Livelihoods: MSMEs help sustain livelihoods, especially for women, youth, and groups in vulnerable situations.
MSME challenges
1. Infrastructure Issues:
Power: Unreliable power supply affects productivity.
Transportation: Poor transport networks hinder supply chain efficiency.
Technology: Limited access to technology and telecommunications slows growth.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Compliance becomes complex as MSMEs expand, increasing administrative burden.
3. Access to Credit: Slow credit disbursal and high interest rates make financing difficult.
4. Technology Constraints: Many MSMEs rely on outdated technology, making it hard to stay competitive.
5. Marketing Challenges: Poor cash flow, lack of expertise, and limited resources hinder marketing efforts.
6. Cash Flow Issues: Inconsistent revenue and delayed payments affect financial stability.
7. Shortage of Skilled Labor: Finding skilled workers for machinery, finance, and marketing remains a challenge.
8. Lack of Innovation: Limited skilled workforce and outdated technology reduce innovation capacity.
Way to improve MSME
1. Financial Access: Easier credit through government guarantees, microfinance, and alternative funding (crowdfunding, invoice discounting).
2. Skill Development: Vocational training, entrepreneurship programs, and sector-specific skill gap analysis.
3. Regulatory Simplification: Streamlined compliance, digitalized processes, and MSME feedback mechanisms.
4. Market Access: B2B platforms, export promotion, and MSME-priority in government procurement.
5. Technology Adoption: Digital tools (ERP, e-commerce), Industry 4.0 (automation, IoT), and digital literacy training.
6. Innovation Support: Incubators, R&D grants, and IP protection for MSME innovations.
Conclusion
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a pivotal role in India’s economic development, contributing significantly to GDP, exports, and employment. The government’s revised MSME classification and various support initiatives aim to enhance financial access, streamline regulations, and encourage technology adoption. Despite challenges like infrastructure bottlenecks, regulatory complexities, and credit constraints, targeted improvements in funding, skill development, and innovation can drive sustainable growth. Strengthening MSMEs will not only boost entrepreneurship but also enhance India’s global competitiveness and economic resilience.
Download Plutus IAS Current Affairs (Eng) 04th Mar 2025
Prelims Questions:
Q. With reference to the MSME sector in India, consider the following statements:
1. The revised MSME classification in the Union Budget 2025 has increased both the investment and turnover limits for all categories of MSMEs.
2. MSMEs contribute to more than 50% of India’s total exports.
3. The Udyam Assist Platform, launched in 2023, aims to formalize Informal Micro Enterprises (IMEs) for priority sector lending benefits.
How many of the above-given statements are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None
Answer: B
Mains Questions:
Q. Discuss the significance of MSMEs in India’s economic growth and employment generation. Highlight key challenges faced by MSMEs and suggest measures to overcome them. (250 words, 15 marks)




No Comments