14 Aug Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)”. The topic “Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)” has relevance in the “Science and Technology” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What is Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)?
What are its applications?
For Mains:
GS3: Awareness in the field of space
Why in the news?
The Department of Space informed the Parliamentary Committee on Science and Technology that the Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) will soon be integrated into Aadhaar enrolment devices.
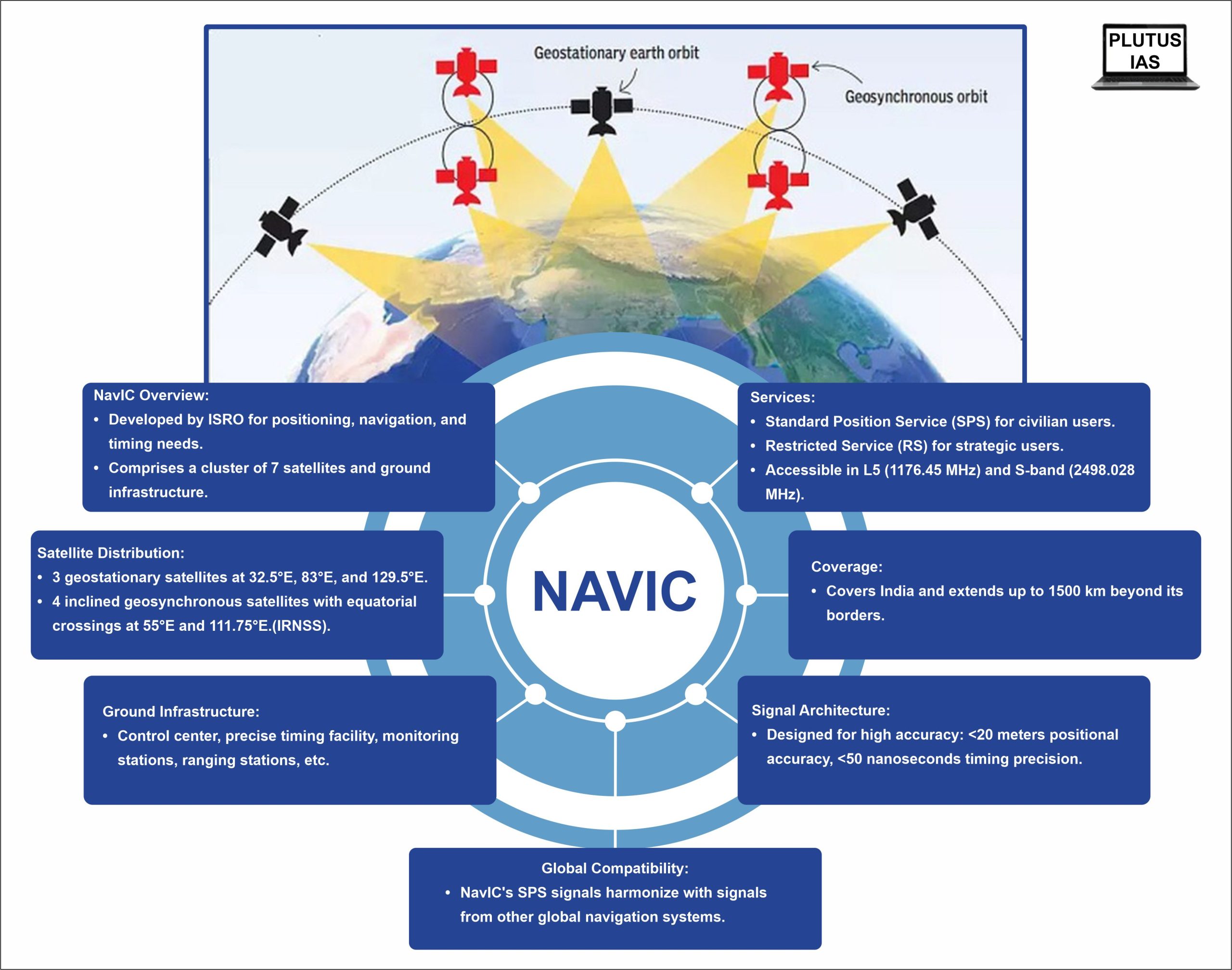
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed the Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC), a regional navigation satellite system, to address the positioning, navigation, and timing needs of the nation.
- Formerly known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), NavIC employs a cluster of 7 satellites and a network of continuous ground stations.
- Among these, three satellites are positioned in geostationary orbit at 32.5°E, 83°E, and 129.5°E respectively.
- The remaining four satellites are located in an inclined geosynchronous orbit, with equatorial crossings at 55°E and 111.75°E and an inclination of 29°—two satellites in each orbital plane.
- Ground Infrastructure:
- The comprehensive ground infrastructure comprises
- a control center,
- precise timing facility,
- range and integrity monitoring stations,
- two-way ranging stations, among others.
- The comprehensive ground infrastructure comprises
- NavIC furnishes two primary services:
- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users
- Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- These services are accessible in both L5 (1176.45 MHz) and S-band (2498.028 MHz).
- The coverage area of NavIC encompasses India and extends up to 1500 km beyond its borders.
- The NavIC signal architecture is meticulously designed to ensure user positional accuracy surpassing 20 meters and timing precision better than 50 nanoseconds.
- Notably, NavIC’s SPS signals harmonize with the signals of other global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) like GPS, Glonass, Galileo, and BeiDou.
- NavIC’s span encompasses a range of applications, including terrestrial, aerial, and marine transportation, location-based services, individual mobility, resource monitoring, surveying, geodesy, scientific research, time synchronization, and the distribution of safety-of-life alerts.
Advantages of having a Regional Navigation System
Distinct Coverage Advantage:
- India boasts the unique advantage of possessing a regional satellite-based navigation system, setting it apart from other nations. This distinction is highlighted when comparing it to the global navigation systems like GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and Beidou.
- Similar to India’s system, Japan operates its own system called GAGAN, which augments GPS signals within its national boundaries.
Enhanced Accuracy and Precision:
- The NavIC system brings forth a notable enhancement in accuracy and precision compared to other navigation systems.
- Its open signals are projected to achieve an impressive accuracy level of around 5 meters, while the restricted signals offer even higher precision.
- In contrast, GPS signals, which are commonly used, typically provide an accuracy of approximately 20 meters.
Strategic Ground Stations:
- Efforts are currently underway to establish additional ground stations in locations such as Japan, France, and Russia.
- The purpose behind these endeavors is to optimize signal triangulation, which in turn enhances the overall performance and reliability of the NavIC system.
Extensive Coverage Area:
- NavIC’s coverage area spans comprehensively across the Indian landmass, offering navigation services within the national borders.
- Furthermore, its influence extends beyond the country’s boundaries, covering an expansion radius of up to 1,500 kilometers.
- This anticipated range ensures that NavIC signals will be accessible even in challenging or remote regions that are traditionally harder to reach.
Geostationary Orbit Advantage:
- The NavIC satellites are positioned in a high geostationary orbit, which brings a distinct advantage. Unlike other satellite systems, the NavIC satellites move at the same rotational speed as the Earth, enabling them to consistently observe and cover the same geographical area.
- In contrast, the satellites used in systems like GPS operate in medium Earth orbits, resulting in varying positions relative to the Earth’s surface.
Signal Path Accessibility:
- One of the noteworthy benefits of NavIC lies in the way its signals enter India’s territory. These signals arrive at a perpendicular 90-degree angle, allowing them to effectively penetrate various environments.
- This includes congested urban areas, dense forests, and even mountainous terrains. On the other hand, GPS signals approach India at an oblique angle, which can sometimes limit their accessibility in challenging terrain.
Exploring Expansion:
- As the usage of NavIC continues to grow, there is a growing interest in expanding the coverage area of the system.
- To this end, the government is actively initiating studies and assessments to evaluate the technical feasibility and parameters involved in such an expansion. This demonstrates the forward-thinking approach aimed at maximizing the benefits of the NavIC navigation system.
As India’s usage of NavIC continues to expand, the ongoing exploration of system expansion underscores the nation’s commitment to harnessing cutting-edge technology for its growth and development, showcasing its determination to lead in space-based navigation services on a global scale.
Sources: Indian GPS NavIC to link to Aadhaar enrolment devices – The Hindu
Q1. Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (UPSC CSE Prelims 2023 Previous Year Question)
(a) Australia
(b) Canada
(c) Israel
(d) Japan
Answer: (d)
Q2. Consider the following:
- NavIC provides two primary services – the Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and the Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- The coverage area of NavIC is limited to India and does not extend beyond its borders.
- NavIC’s signal architecture is designed to achieve user positional accuracy of over 20 meters and timing precision of better than 50 nanoseconds.
How many of the abovementioned statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: (b)
Q3. Discuss the distinctive features and advantages of the Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) in comparison to other global navigation systems. How does its unique design contribute to improved accuracy, coverage, and accessibility?




No Comments