24 Jul Neoclassical Theories
Neoclassical Theories – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Complete Notes with Models, Diagrams, Infographics, Mind Map, PYQs & Probable Questions
Introduction
The Neoclassical school of economics emerged in the late 19th century as a refinement of Classical theories. It emphasizes individual choice, marginalism, and market equilibrium. Prominent economists like William Stanley Jevons, Carl Menger, Léon Walras, Alfred Marshall, and Vilfredo Pareto contributed to this paradigm, which continues to shape modern microeconomic analysis.
Core Assumptions of Neoclassical Theories
- Economic agents are rational and seek to maximize utility (consumers) or profit (producers).
- All markets operate under perfect competition.
- Consumers and producers have perfect information.
- Resources are scarce and allocation is determined by price mechanisms.
- Utility and production are continuous and differentiable.
Key Components of Neoclassical Theory
1. Theory of Value and Price (Marginal Utility Theory)
Value is determined not by total utility but by the marginal utility of the last unit consumed. Consumers allocate their income to maximize total utility subject to a budget constraint.
- Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: As more units of a good are consumed, the additional satisfaction derived decreases.
- Equi-Marginal Principle: Consumers balance marginal utility per unit of money across goods.
2. Consumer Behavior and Demand Theory
Neoclassical economists introduced the concept of indifference curves and budget constraints to derive individual demand curves.
- Utility is ordinal and represented by indifference curves.
- Consumer equilibrium occurs where an indifference curve is tangent to the budget line.
3. Theory of Production and Cost
Firms aim to minimize cost or maximize output given the production function:
- Short-run and long-run production functions
- Law of Variable Proportions
- Returns to scale
4. Marginal Productivity Theory of Distribution
Each factor of production is paid according to its marginal product. Under perfect competition, the wage rate equals the marginal product of labor (MPL) and rent equals the marginal product of land (MPLand), and so on.
5. General Equilibrium (Walrasian Model)
Developed by Léon Walras, it describes simultaneous equilibrium in all markets through a system of equations. This ensures that supply equals demand across goods and factor markets.
6. Welfare Economics
Neoclassical theories extended to welfare economics with the Pareto Efficiency concept. An allocation is Pareto optimal if no one can be made better off without making someone else worse off.
Mind Map – Neoclassical Theories
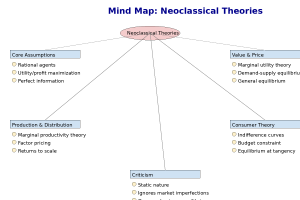
Neoclassical Theories MindMap
Infographic – Overview of Neoclassical Concepts
Criticism of Neoclassical Theory
- Unrealistic assumptions: Perfect competition and information rarely exist in reality.
- Ignores institutional factors: Power structures, culture, and policy interventions are sidelined.
- Static nature: Focuses on equilibrium rather than dynamic processes.
- Inability to explain crises: Neoclassical models failed to predict or explain major economic crises like the 2008 financial crash.
Contributions of Key Economists
- Jevons, Menger, Walras: Marginal utility theory of value.
- Alfred Marshall: Partial equilibrium, price elasticity, consumer surplus.
- Pareto: Welfare optimum, ordinal utility.
- Edgeworth: Indifference curves and contract curves.
Applications in Policy and Real World
- Explains consumer choice and market demand.
- Basis for pricing and cost control strategies.
- Used in welfare programs through cost-benefit analysis.
- Supports market-friendly reforms like deregulation and privatization.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs) – UPSC CSE Economics Optional
- 2023: Explain how Neoclassical theory differs from Classical theory in the context of value and distribution.
- 2020: Discuss the assumptions and implications of Marginal Productivity Theory of Distribution.
- 2018: How does indifference curve analysis improve upon marginal utility analysis in explaining consumer behavior?
Probable Questions for UPSC
- Mains: “Neoclassical economics assumes a frictionless market.” Critically examine this statement.
- Mains: How does General Equilibrium analysis help in understanding interconnected markets?
- Prelims: Which of the following is NOT an assumption of Neoclassical theory?
a) Rational agents
b) Homogeneous products
c) Government intervention
d) Perfect informationAnswer: c) Government intervention
Conclusion
Neoclassical theory remains foundational in economic thought, providing tools for understanding market behavior, resource allocation, and policy design. For UPSC aspirants, mastering its assumptions, models, and limitations ensures a strong base in Microeconomics, helping in both conceptual clarity and scoring high in Paper 1 of Economics Optional.




No Comments