03 Mar Neutrinos
Neutrinos
This article covers “Daily current Affairs for UPSC “and the topic is about ‘Neutrinos’ which is in the news, it covers “Science and Technology” In GS-3, the following content has relevance for UPSC.
For Prelims: Neutrinos
For Mains: GS-3, Science and Technology
Why in news: Recently, a Japanese experiment stated that it was unable to uncover “strong evidence” that this is the case, ruling out a few theories that attempted to explain the myriad strange behaviors of neutrinos.
About Neutrinos
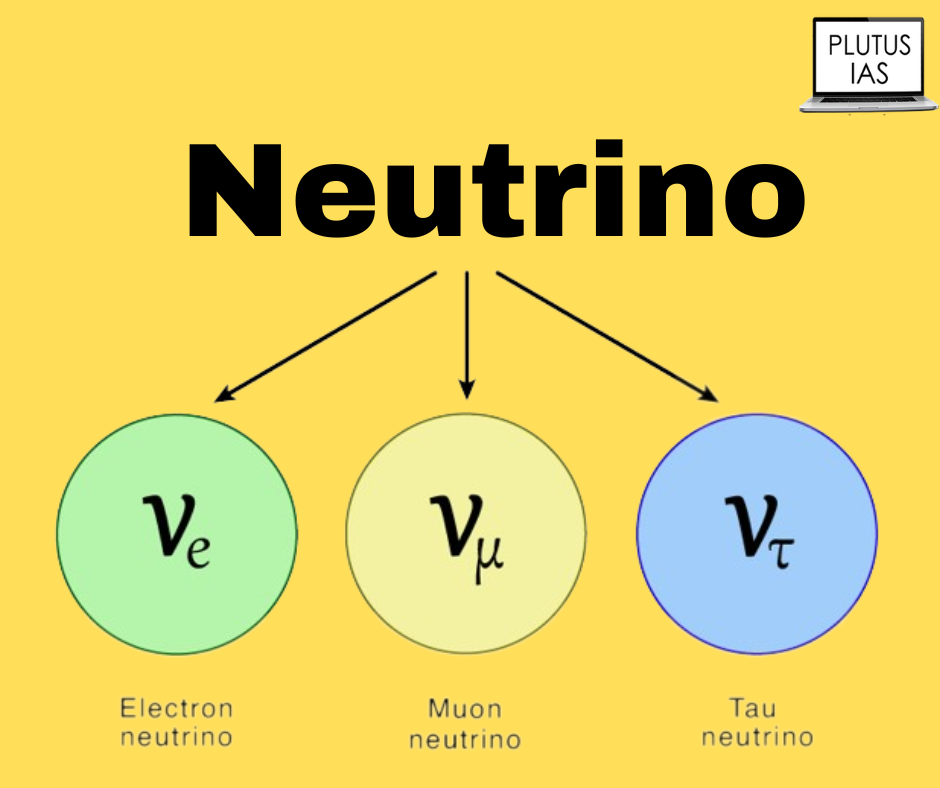
- A neutrino is a subatomic particle that resembles an electron in many ways but differs in that it lacks an electrical charge and has a very small mass that might potentially be zero.
- One of the most prevalent particles in the universe is the neutrino.
- They barely interact with matter; they are exceedingly hard to find.
- Both electrons and neutrinos are treated similarly by nuclear forces; neither participates in the strong nuclear force, but both do so equally in the weak nuclear force. Leptons are particles with this characteristic.
- The muon, which has a mass 200 times more than that of the electron, and the tau, which has a mass 3,500 times greater than that of the electron, are two further charged leptons in addition to the electron (and its antiparticle, the positron).
- Like the electron, the muon and tau also have companion neutrinos known as muon-neutrinos and tau-neutrinos.
- Scientists refer to this transition between neutrino kinds as neutrino oscillation.
Neutrinos
Discovery
- In 1930, Wolfgang Pauli made the initial hypothesis regarding the neutrino’s existence.
- There was difficulty at that time since it appeared that beta decay did not conserve energy and angular momentum.
- But Pauli argued that one could restore the conservation rules if a neutral, non-interacting particle—a neutrino—were released.
- It wasn’t until Clyde Cowan and Frederick Reines documented antineutrinos released by a nuclear reactor in 1955 that neutrinos were first discovered.
Sources
- The radioactive disintegration of primordial elements within the planet, which produces a significant flux of low-energy electron-antineutrinos, is one of the neutrinos’ natural sources.
- According to calculations, the sun’s fusion events release neutrinos that take away around 2% of the sun’s energy.
- Because only neutrinos can enter the extremely dense material created by a collapsing star, supernovae are also primarily a neutrino phenomenon. Just a small portion of the available energy is converted to light in supernovae.
India-based Neutrinos Observatory
- It is planned to establish the India-based Neutrino Observatory in Tamil Nadu’s Theni area.
- A particle physics research project is being built in a cave beneath a mountain that is 1,200 meters (3,900 feet) deep with the main goal of studying atmospheric neutrinos.
- The Iron-Calorimeter Detector is the primary experiment that INO has put forth.
Concern on Neutrino
- If the project is carried out, it will have an impact on the plants and animals in the Western Ghats’ Periyar Tiger Reserve and Mathikettan Shola National Park, two places known for their effective conservation efforts.
- As a result, the Tamil Nadu government will not approve of its development.
Why is the mountain necessary to INO?
- Most of the charged particles from the cosmic rays are filtered out by the mountain’s 1 km of solid rock.
- A portion of the incident cosmic ray protons, pions, and nearly all of the neutrinos make up the filtered set.
Why must these trials be conducted underground?
- The detector would detect roughly 10 neutrino occurrences per day and billions of cosmic ray muons per hour if it were positioned near the mountain’s base.
- After being inserted into the rock, it would only be able to detect roughly 10 neutrinos per day and 300 muon events per hour, of which 3 would be the needed muon neutrino events.
How does the Iron Calorimeter identify the neutrinos?
- Iron slabs alternately cover 150 layers to form the ICAl.
- A muon that is electrically charged is created as a result of the muon neutrino’s interaction with the iron.
- Sensitive elements detect this charge.
- The path taken by the muon is traced by combining the pulses.
- From this, one can deduce the characteristics of the neutrino that generated the pulses.
Source:
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
The topic described above is related to daily current affairs which are based on science and technology. The UPSC aspirants get such kinds of the latest and best daily current affairs based on Science and technology for the UPSC exam preparation from Plutus IAS. Also, read weekly and monthly current affairs for your IAS exam preparation.
Download the PDF now:



No Comments