14 Oct Ozone Hole
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Ozone Hole”. This topic has relevance in the “Environment and Ecology” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What is an Ozone Hole?
For Mains:
GS2: Environment and Ecology
Why in the news?
Satellite data from the European Space Agency’s Copernicus Sentinel-5P has identified a massive ozone hole over Antarctica, measuring 26 million square kilometres, about three times the size of Brazil, as part of the EU’s environmental monitoring program.
About Ozone
- Ozone (O3) is a triatomic molecule composed of three oxygen atoms, and it is a dynamic component of Earth’s atmosphere.
- Most ozone resides in the stratosphere at altitudes ranging from approximately 10 to 50 kilometres above the Earth’s surface.
- Its critical role lies in absorbing and filtering out most of the harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, specifically UV-B and UV-C, emitted by the sun.
- This function is vital for protecting life on Earth from the harmful effects of excessive UV radiation, including skin cancer, cataracts, and damage to the DNA of living organisms.
Production of ozone
- Ozone is primarily produced in the stratosphere through a complex photochemical process. Ultraviolet (UV-C) radiation, which is more energetic and prevalent in the upper stratosphere, photodissociates molecular oxygen (O2), resulting in the formation of atomic oxygen (O).
- The atomic oxygen then reacts with molecular oxygen to produce ozone. This ozone production occurs most efficiently in the upper stratosphere, where UV-C radiation is the most intense.
- The ozone layer is in a state of dynamic equilibrium, with production and destruction processes continually occurring.
Ozone Hole
- The term “ozone hole” refers to a localised and severe depletion of ozone concentrations within the stratosphere, often occurring in polar regions, such as Antarctica.
- Ozone holes are primarily associated with releasing synthetic ozone-depleting (ODS) compounds, including chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons.
- These ODS are transported to the stratosphere, broken down by UV- C radiation, releasing chlorine and bromine atoms. These atoms catalytically destroy ozone molecules.
- As a result, the ozone layer becomes thinner in these areas, allowing higher levels of harmful UV radiation to penetrate the Earth’s surface, leading to detrimental environmental and health effects.
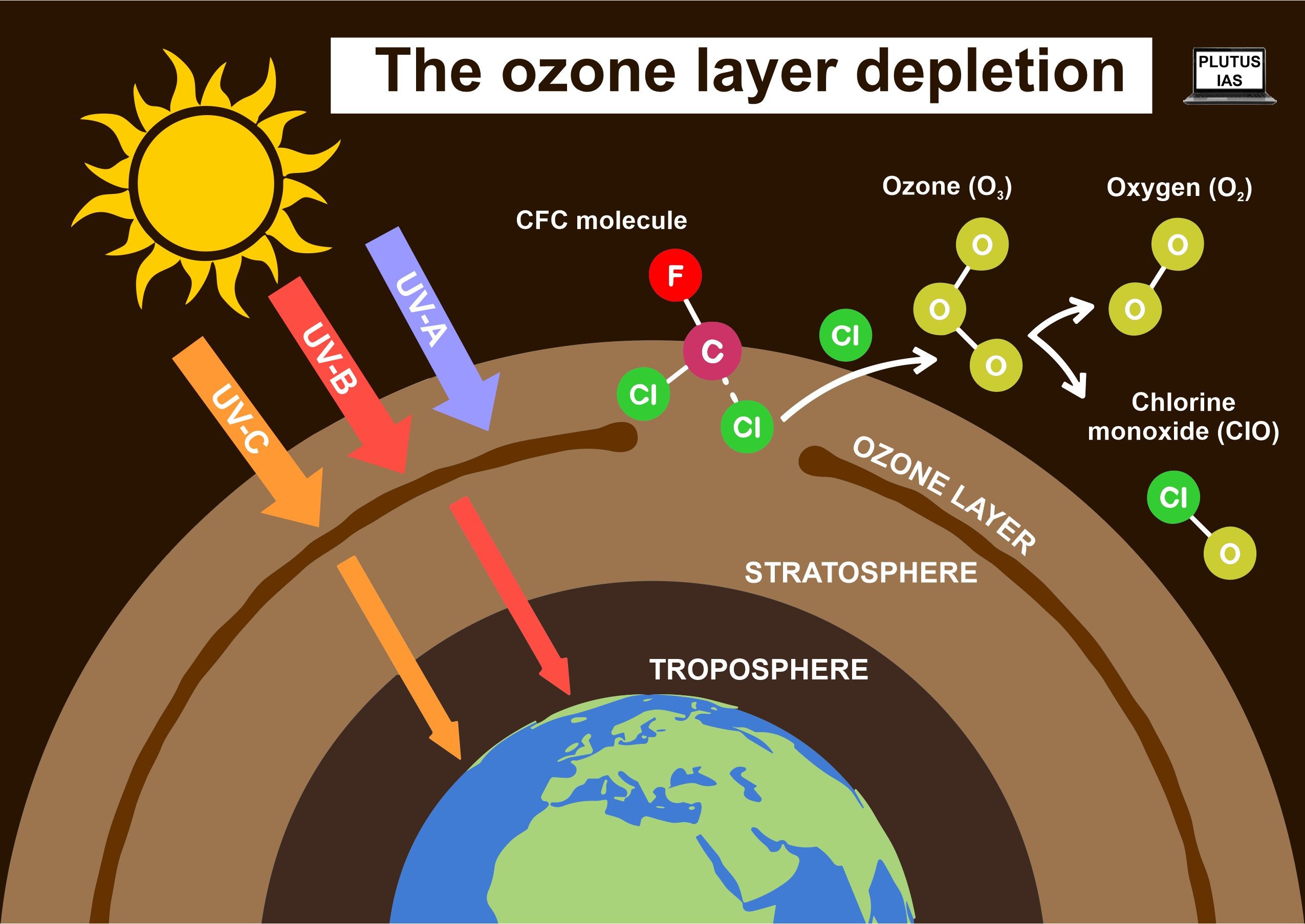
Causes of recent ozone hole over Antarctica
- The giant ozone hole observed this year over Antarctica is believed to be caused by volcanic eruptions at Hunga Tonga in Tonga that occurred in December 2022 and January 2023.
- These eruptions released water vapour into the stratosphere, which impacted the ozone layer through chemical reactions and changed its heating rate.
- The water vapour also contained elements like bromine and iodine, which can deplete ozone.
- Although human activities have been responsible for ozone depletion in the past, there isn’t much evidence to suggest that this year’s ozone hole is due to human causes.
Climate Change and Ozone
- Impact of Rising Temperatures and Ozone Holes: While ozone depletion isn’t a primary cause of climate change, rising global temperatures can affect ozone hole formation and dynamics, leading to complexities in atmospheric conditions.
- Unusual Ozone Hole Behavior: Recent anomalies like the extended 2020 ozone hole are linked to factors like wildfires and increased stratospheric smoke from more intense and widespread fires.
- Ozone Depletion Due to Climate Change: With the ongoing climate crisis, more frequent and severe global wildfires could intensify ozone depletion, posing ozone management and mitigation challenges.
- Ozone Holes’ Impact on Earth’s Climate: Ongoing research suggests that ozone holes may have cooling effects by reducing the greenhouse gas effect. However, their interactions with climate dynamics remain intricate.
- Altered Season Duration: Ozone depletion, primarily in polar regions, can prolong winter seasons by maintaining the polar vortex, influencing ecosystems and atmospheric circulation patterns.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 14th Oct 2023
Q1. With reference to Ozone holes, consider the following statements:
- Ozone holes majorly occur in the equatorial regions due to high insolation.
- They are primarily associated with chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons.
- The ozone layer is in a dynamic equilibrium state, with production and destruction processes occurring continuously.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) None
Q2. Huga Tonga volcano is located in which of the following seas/ oceans?
(a) Atlantic Ocean
(b) Indian Ocean
(c) Pacific Ocean
(d) Black Sea
Q3. Examine the role of ozone in Earth’s atmosphere, the processes involved in its production, and the ozone depletion phenomenon.



No Comments