23 Jul Physical conditions of the earth’s interior
Physical Conditions of the Earth’s Interior – UPSC Geography Optional
Introduction
Understanding the physical conditions of the Earth’s interior is a foundational topic in geomorphology and physical geography. It provides insight into geodynamic processes like plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanism, and mountain building. These internal forces are vital for shaping the Earth’s surface and influencing its evolution over geological time scales.
Earth’s Interior Explained
1. Sources of Information about Earth’s Interior
- Seismic Waves: P-waves and S-waves help determine the state and composition of internal layers.
- Gravitational Studies: Variations in gravity help infer density distribution.
- Magnetic and Electrical Studies: Help map subsurface structures.
- Volcanic Materials: Magma and gases give direct evidence of mantle and crustal composition.
- Meteorites: Provide clues about Earth’s core composition.
- Deep Drilling Projects: Scientific efforts like the Kola Superdeep Borehole provide data, albeit limited.
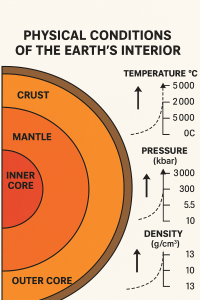
2. Temperature in Earth’s Interior
- Geothermal Gradient: Average increase of 25–30°C per km in the crust.
- Mantle and Core: Estimated temperatures exceed 3000°C in the mantle and 5000–6000°C in the inner core.
- Heat Sources: Residual heat from Earth’s formation, radioactive decay, and gravitational compression.
3. Pressure in Earth’s Interior
Pressure increases with depth due to the weight of overlying rocks.
- At the crust-mantle boundary: ~10,000 atm
- At the core-mantle boundary: ~1.3 million atm
- At the center of the Earth: ~3.6 million atm
Earth’s Interior Explained
4. Density Distribution
Density also increases with depth:
- Continental Crust: ~2.7 g/cm³
- Oceanic Crust: ~3.0 g/cm³
- Mantle: ~3.3–5.5 g/cm³
- Core: ~10–13 g/cm³
This gradient is largely due to the increasing pressure and heavier materials in deeper layers.
Best ias coaching in hindi medium
Best mentorship programme for upsc
Best ias coaching in chandigarh
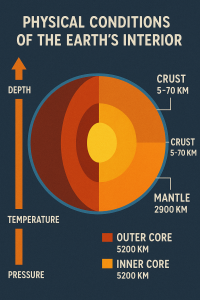
5. Composition of Earth’s Layers
- Crust: Silicate minerals rich in aluminum (continental) and magnesium (oceanic)
- Mantle: Ferro-magnesium silicates (olivine, pyroxenes)
- Outer Core: Liquid iron-nickel alloy
- Inner Core: Solid iron-nickel due to immense pressure
6. Mechanical Layers Based on Physical Properties
- Lithosphere: Rigid upper mantle + crust (~100 km thick)
- Asthenosphere: Semi-fluid layer enabling plate movement
- Mesosphere: Rigid lower mantle
- Outer Core: Liquid state, responsible for Earth’s magnetism
- Inner Core: Solid state due to pressure dominance
7. Seismic Behavior of Internal Layers
- P-Waves: Travel through solids and liquids, fastest seismic waves
- S-Waves: Only travel through solids; absence in outer core confirms liquid state
- Shadow Zones: Provide evidence for layering (e.g., P-wave shadow confirms core; S-wave shadow confirms liquid outer core)
8. Previous Year UPSC Questions
- 2020: Explain the behavior of seismic waves and what they reveal about the Earth’s internal structure.
- 2017: Describe the composition and physical conditions of the Earth’s interior layers.
- 2015: How do variations in pressure and temperature affect rock behavior in the Earth’s interior?
9. Probable Questions for UPSC Prelims & Mains 2025
- Discuss the significance of the asthenosphere in plate tectonics.
- Explain the variation of temperature, pressure, and density inside the Earth.
- Why is the inner core solid despite high temperatures?
- Compare and contrast the continental crust and oceanic crust in terms of composition and thickness.
- What causes the shadow zone in seismic studies and what does it reveal?
10. Conclusion
The physical conditions of Earth’s interior—temperature, pressure, density, and composition—play a vital role in driving internal processes like volcanism, mountain-building, and tectonic movements. These dynamic processes are integral to understanding the Earth’s evolution and the formation of various landforms. A thorough grasp of this topic is essential for any aspirant opting for Geography in UPSC CSE.
Best geography optional coaching
Best geography optional teacher




No Comments