16 Oct PM Gati Shakti: Transforming India’s Infrastructure and Connectivity
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-Economics-PM Gati Shakti: Transforming India’s Infrastructure and Connectivity
FOR PRELIMS
How does PM Gati Shakti contribute to the overall economic development of India.
FOR MAINS:
Analyze how the PM Gati Shakti initiative can drive economic growth in India. What specific sectors are likely to benefit the most, and why?
Why In the News?
The Prime Minister of India has emphasized the significance of the PM Gati Shakti Master Plan as it marks the completion of three transformative years. This ambitious initiative aims to enhance infrastructure and streamline connectivity across the nation, fostering economic growth and development.

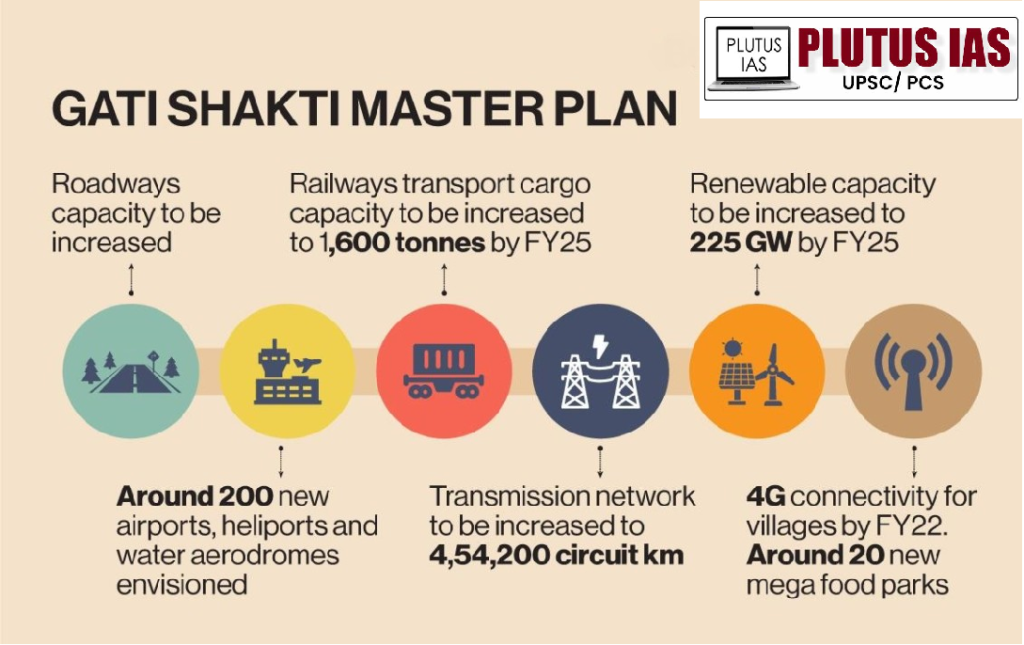
PM Gati Shakti:
PM Gati Shakti is a key initiative by the Government of India aimed at enhancing infrastructure and connectivity. It features the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, which integrates data from 44 Central Ministries and 36 States/UTs, streamlining planning and execution. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) ensure data accuracy across key sectors. The initiative has evaluated 208 major projects worth Rs. 15.39 lakh crores and assessed projects under three economic corridors. 
Key facts:
1. Launch Date: The initiative was launched on October 13, 2021.
2. National Master Plan (NMP): Aims to create a comprehensive framework for integrated infrastructure planning and execution.
3. Data Integration: Involves 1,614 data layers from 44 Central Ministries and 36 States/UTs.
4. Project Evaluation: An assessment of 208 major infrastructure projects worth Rs. 15.39 lakh crores has been conducted.
5. Economic Corridors: Focuses on projects in Energy, Mineral, Cement, High Traffic Density, and Rail Sagar corridors.
6. Achievements:
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) planned over 8,891 km of roads using NMP.
The Ministry of Railways (MoR) planned more than 27,000 km of railway lines and accelerated the completion of Final Location Surveys (FLS), completing 449 FLS in FY ’22 compared to 57 in FY ’21.
The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoPNG) streamlined the Detail Route Survey (DRS), reducing report creation time from 6-9 months to just one day using electronic DRS (eDRS).
7. Sectors Involved:
Transport: Railways, roads, and ports.
Energy: Renewable and conventional energy projects.
Urban Development: Smart cities and urban infrastructure.
Telecommunications: Improving digital connectivity.
Social Infrastructure: Health, education, and housing sectors.

8. Committees:
Inter-Ministerial Coordination Committee: Facilitates collaboration among various ministries.
Technical Advisory Committee: Provides expertise on project planning and execution.
Monitoring Committees: Oversee project implementation and adherence to SOPs.
Last three-year Achievements:
1. Government Integration: Onboarded 44 Central Ministries and 36 States/UTs onto a unified platform with 1,600+ data layers.
Evaluated 200+ major infrastructure projects based on integrated planning principles.
2. Social Sector Development: Extended PM GatiShakti to Social Sector Ministries to identify gaps in infrastructure like schools and hospitals.
Developed applications for improved planning in healthcare, education, and tribal development.
3. State Master Plans: All 36 States/UTs developed PM GatiShakti State Master Plan (SMP) portals, mapping 533 projects.
Enhanced regional development and capital investment streamlining.
4. Logistics and Trade Facilitation: Aligned with the National Logistics Policy to reduce logistics costs and improve India’s Logistics Performance Index (LPI), which rose from 44 to 38 in 2023.
5. Stakeholder Engagement: Conducted five regional workshops for knowledge sharing across all States/UTs, fostering cooperative federalism.
6. Data-Driven Development: Implemented GIS-based tools for real-time monitoring, ensuring timely project completion and reducing delays.
7. Training and Capacity Building: Over 20,000 officials trained on PM GatiShakti, with courses integrated into Central Training Institutes’ curricula.
Conducted 150+ interactive training sessions with various ministries and states.
8. District-Level Planning:
Developing PM GatiShakti District Master Plan (DMP) portal for collaborative planning at the district level, incorporating AI and IoT.
9. International Collaboration:
Engaged with countries like Nepal, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka to promote PM GatiShakti and geospatial technologies for infrastructure planning.
10. National Logistics Policy Highlights
Policy Launch: Launched on September 17, 2022, to create an efficient, cost-effective logistics network.
State Logistics Plans: 26 States/UTs have aligned with the NLP by notifying their own State Logistics Policies.
LEADS Survey: Fifth and sixth editions of the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) report released, assessing logistics ease in various states.
Unified Logistics Integrated Platform (ULIP): Integrated 33 logistics-related systems across 10 ministries, facilitating real-time cargo tracking and innovation.
Logistics Data Bank (LDB): Developed to track 100% of containerized EXIM cargo using RFID and IoT technologies, offering cloud-based visualization.
LPI Improvement Strategy: Dedicated action plan involving multiple ministries to enhance logistics efficiency and address challenges.
Global Collaboration: Partnered with the Asian Development Bank and engaged with the World Bank to adopt best practices for logistics improvement.

Persistent Issues in Infrastructure Under PM Gati Shakti:
1. Data Sharing Problems: Different ministries and states still struggle to share data effectively, leading to inefficiencies.
2. Training Shortcomings: Although training programs exist, many local officials lack the necessary skills to implement projects effectively.
3. Project Delays: Bureaucratic challenges and land acquisition issues often slow down project timelines.
4. Funding Limitations: Many states face difficulties in securing the necessary funds for large infrastructure projects.
5. Uneven Development: Infrastructure improvements vary widely between regions, leaving some areas behind.
6. Sustainability Issues: While there’s a focus on green infrastructure, actual implementation of sustainable practices is inconsistent.
7. Coordination Challenges: Better collaboration is needed among central and state governments, private sectors, and local communities.
8. Monitoring Gaps: A stronger framework is required to track project progress and evaluate outcomes effectively.
9. Technology Use: While advanced tools like GIS are part of the plan, many officials still struggle to use them effectively.
Potential Solutions for Sustainable Development Under PM Gati Shakti:
1. Enhanced Data Integration: Develop a centralized data-sharing platform that facilitates seamless integration and access to data across all ministries and states.
2. Targeted Training Programs: Implement ongoing, tailored training initiatives for local officials and stakeholders to build capacity in project management and technology use.
3. Streamlined Approval Processes: Simplify bureaucratic procedures and enhance coordination between departments to expedite land acquisition and project approvals.
4. Innovative Funding Mechanisms: Explore public-private partnerships (PPPs) and other financial models to attract investment and diversify funding sources for infrastructure projects.
5. Balanced Regional Development: Prioritize infrastructure projects in underdeveloped areas to ensure equitable growth and connectivity across all regions.
6. Sustainability Guidelines: Establish clear sustainability guidelines and standards for all infrastructure projects to promote the use of eco-friendly materials and practices.
7. Strengthened Stakeholder Collaboration: Foster regular dialogue and partnerships between government entities, the private sector, and local communities to ensure collective ownership of projects.
8. Robust Monitoring Framework: Create a comprehensive monitoring and evaluation system to track project progress, identify challenges early, and measure sustainability outcomes.
9. Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch campaigns to educate the public about the benefits of infrastructure projects, encouraging community involvement and support.
10. Promotion of Smart Technologies: Encourage the adoption of smart technologies, such as IoT and AI, for real-time monitoring and management of infrastructure projects.
Conclusion:
The PM Gati Shakti initiative represents a transformative approach to infrastructure development in India, aiming to create a seamless and efficient multimodal transportation network. By integrating the efforts of various ministries and leveraging advanced technologies, this initiative seeks to enhance connectivity and reduce logistics costs across the nation. The Gati Shakti Sanchar portal further supports this vision by streamlining the Right of Way approvals process, accelerating telecom infrastructure rollout, and facilitating the rapid deployment of 5G services across the country. With these combined efforts, India is well-positioned to achieve its ambitious goals of Aatmanirbharta.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 16th Oct 2024
Prelims Question:
Q.Consider the following statements about PM Gati Shakti:
1. PM Gati Shakti integrates various ministries and state departments to enhance infrastructure planning and execution.
2. The initiative aims to improve India’s Logistics Performance Index (LPI) by 10 positions by 2025.
3. PM Gati Shakti includes provisions for public-private partnerships to encourage investment in infrastructure projects.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None
Answer:B
Mains Question:
Q.Discuss the significance of the PM Gati Shakti initiative in transforming India’s infrastructure and connectivity. Evaluate its potential impact on economic growth, regional development, and sustainable practices in infrastructure planning.
(250 words, 15 marks)




No Comments