24 Jan Ram Temple
Ram Temple
This article covers ‘Daily Current Affairs’ and the topic details of “Ram Temple’’. This topic is relevant in the “Indian Culture” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
UPSC MAINS GS1 Syllabus: Architecture from Ancient to Modern times
Why in the News?
With the opening of the Ram temple in Ayodhya on January 22, 2024, a 200-year-old tale that had a significant influence on India’s sociopolitical climate came to an end. The Nagara Style of temple architecture is used in the design of the Ram temple.
About Timeline of Ram JanmaBhoomi Movement
- The campaign acquired impetus in the 19th century after the Marathas filed an appeal for control over Ayodhya, Kashi, and Mathura in 1751. Court documents from 1822 describe a mosque on the site of Lord Ram’s birth.
- Tensions rose in 1855 after a violent battle between Hindus and Muslims near the Babri Masjid, which resulted in the Hindus taking over Janmasthan.
- In 1949, the idol of Ram Lalla was placed in the mosque, generating calls for a large shrine.
Legal Battles
- The Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP) launched a ‘liberation’ drive for Ram Janmabhoomi, Krishna Janmabhoomi, and the Vishwanath shrine in the 1980s.
- Legal fights occurred, and in 1986, the Babri Masjid’s locks were released, allowing Hindus to pray.
- Significant events occurred in the years that followed, including the 1989 foundation-laying ceremony and the 1990 Rath Yatra organised by LK Advani, which sparked major riots.
Demolition of the Babri Masjid
- On December 6, 1992, a mob razed the Babri Masjid, causing political implications and judicial actions.
- The Acquisition of Certain Areas at Ayodhya Act was passed by Parliament in 1993, authorising the government to take control of the disputed Ram Janmabhoomi-Babri Masjid site.
- In 2009, the Liberhan Commission highlighted the intentional character of the 1992 events.
- In 2019, the Supreme Court gave the contested site to Hindu petitioners for a Ram temple, while allocating land for a mosque nearby.
Important features of Ram Mandir
Main Complex
- Ram Mandir is a Hindu temple located in Ayodhya, Uttar Pradesh. It is located in Ram Janmabhoomi, Lord Rama’s birthplace.
- The grand edifice was built entirely without the use of iron or steel. Stones were gathered from Rajasthan’s Bansi Paharpur region.
- The temple complex, built in the ancient Nagara architecture, will measure 380 feet long from east to west, 250 feet wide, and 161 feet tall.
- Each of the floors of the temple will be 20 feet high, with 392 pillars and 44 gates.
- Around the main temple is a rectangular peripheral known as the percota, which is seen in temples in south India but not in north India.
- Images of Lord Hanuman, other deities, peacocks, and flower patterns have been carved into the stones, giving the edifice a divine appearance.
- More than 3,000 kilograms of flowers from over 20 species were utilised to embellish the enormous edifice.
Entrance
Ornate statues of elephants, lions, Lord Hanuman, and Garuda were erected at the temple’s main gate earlier this month. These statues were likewise made from sandstone sourced from Bansi Paharpur.
What is the Nagara Style of Temple Architecture?
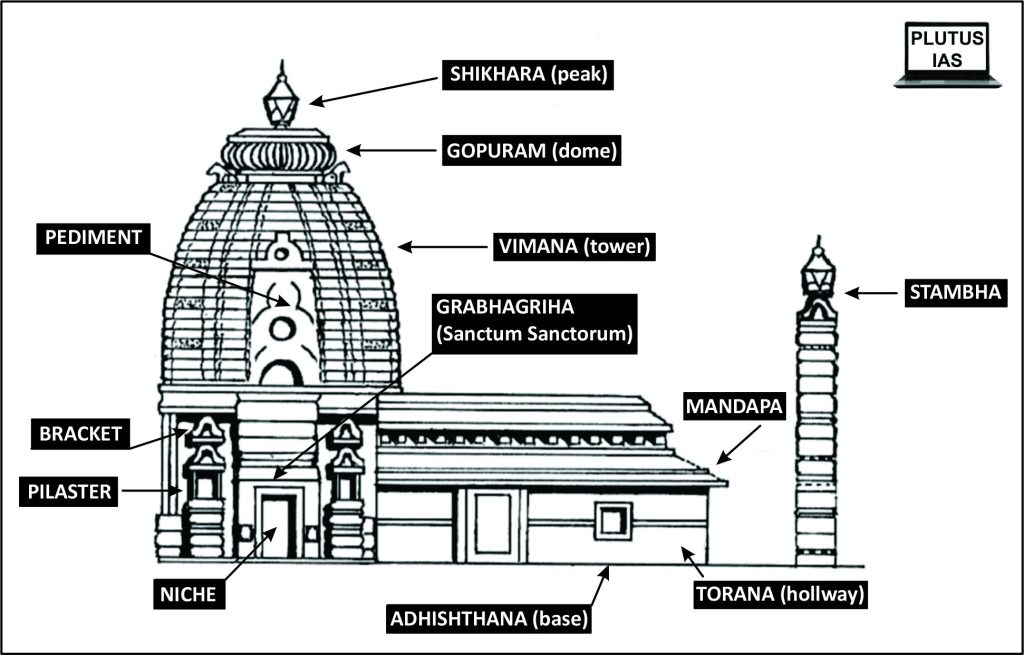
- The Nagara temple architecture style arose in northern India about the 5th century CE, during the late Gupta dynasty. It appears in contrast with the Dravidian style of southern India, which originated around the same time.
- Nagara temples are erected on an elevated platform, having the Garbha Griha (sanctum sanctorum)—where the deity’s idol rests—being the most sacred part of the temple.
- The shikhara (literally mountain peak’) towers over the Garbha Griha and is the most distinguishing feature of Nagara-style temples.
- As the name implies, shikharas are man-made depictions of the natural and cosmological order as conceived in Hindu tradition.
- A typical Nagara-style temple also includes a circumambulatory corridor around the garbha griha, as well as one or more mandapas (halls) aligned with it. Elaborate murals and reliefs frequently cover the walls.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 24th Jan 2024
Prelims practice questions
Q1) Consider the following statements regarding the Nagara style of Temple Architecture?
1) Vimana is the term for the assembly hall in front of the sanctum.
2) Amalaka in Nagar temple architecture is for the decorative ornamentation.
3) Gupta dynasty is often associated with the promotion of Nagara temple architecture.
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) None
ANSWER: B
Q2) Consider the following statements regarding Dravidian temple architecture:
1) Vimana is the term for the assembly hall in front of the sanctum.
2) Amalaka in Dravidian temple architecture serves the purpose of decorative ornamentation.
3) Pallava dynasty is often associated with the promotion of Dravidian temple architecture.
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Mains practice questions
Q1) Compare and contrast Nagara style temples with Dravidian style temples in terms of architecture, layout, and symbolism. Discuss the regional variations and the religious significance associated with each.
Q2) Analyze the role of the Gupta dynasty in the development and patronage of Nagara style architecture. How did the political and cultural milieu of the Gupta period contribute to architectural innovations?
I am a content developer and have done my Post Graduation in Political Science. I have given 2 UPSC mains, 1 IB ACIO interview and have cleared UGC NET JRF too.




No Comments