11 Jan Relationship between Judiciary and Legislature
Relationship between Judiciary and Legislature
This article covers “Daily current Affairs for UPSC” and the topic is about the ‘Relationship between Judiciary and legislature’ which is in the news, it covers the “Separation of power” In GS-2, and the following content has relevance for UPSC.
For Prelims: Separation of power
For Mains: GS -2, Issues and significance of the separation of power
Why in news:
The 83rd All India Presiding Officers Conference will cover topics such as India’s G-20 leadership, the judiciary-legislative relationship, and the efficient operation of Parliament and Assemblies.
About Judiciary and Legislature
The division of a government’s legislative, executive, and judicial responsibilities is known as the separation of powers. Since all three branches must approve for laws to be made, carried out, and administered, it reduces the likelihood of arbitrary government actions.
Any branch of the government is prohibited from concentrating too much power due to constitutional delineation.
Historic Background of the Doctrine of Separation of Powers
- Aristotle, who lived in the 4th century BC, originally introduced the idea of separation of powers in his writings, referring to the General Assembly, Public Officials, and Judiciary as the three branches of government.
- On the current design tenet of separation of powers, John Locke’s (1632–1704) constitutional philosophy was elaborated.
- The work of the philosopher Montesquieu, whose work is based on the English system, was produced in the 18th century and is a highly systematic and scientific theory.
- James Madison, the father of the American constitution, stated that the judicial, executive and legislative branches should all have equal power.
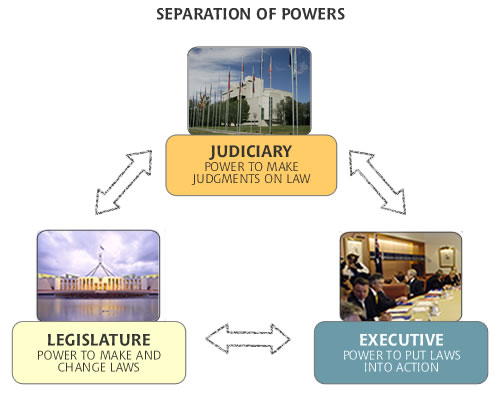
Separation of Powers
Constitutional provisions of the Judiciary and Legislature
- Article 50 states that the state must take action to keep the judiciary and executive branches separate.
- Articles 121 and 211 prohibit discussion of the judicial actions of Supreme Court and High Court judges in the Parliament and State Legislatures.
- Articles 122 and 212 state that no court may challenge the legality of legislative or parliamentary proceedings.
- According to Article 361, neither the President nor the Governor is subject to legal accountability for the way they carry out their official responsibilities.
- The various organs can impose checks on one another through specific provisions in a system of checks and balances.
- For instance the Judicial review, the court has the authority to examine the legislative and executive branches’ acts
- If a statute is unconstitutional or arbitrary as defined by Article 13 of the Constitution, the judiciary has the authority to invalidate it (If it violates Fundamental rights)
- The legislature may examine how the executive is conducting itself.
- The administration appoints judges, who serve in an independent judiciary.
- A system of checks and balances makes sure that no organ gains excessive power.
Judicial Interpretations:
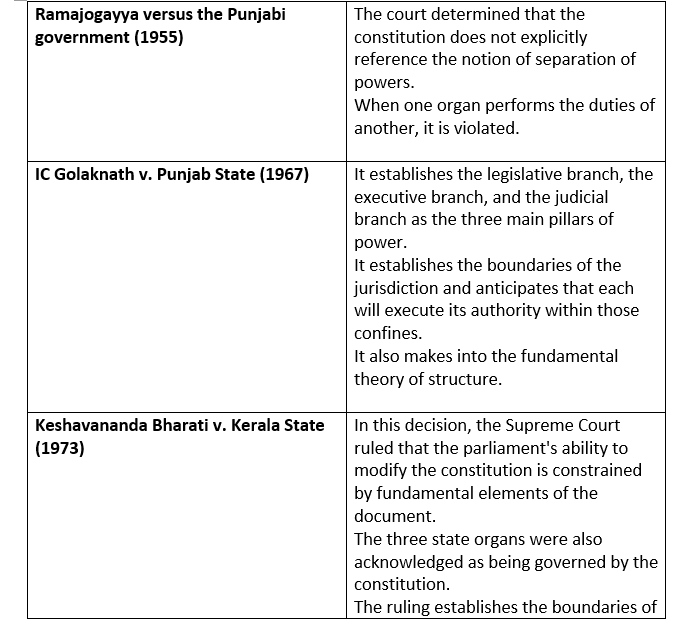
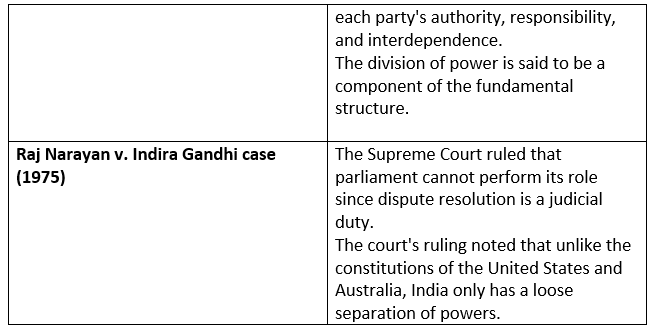
Functional overlapping of Judiciary and Legislature
- Due to the impossibility of tight delineation, each organ tends to encroach on the territory of other functionaries while carrying out its duties.
- For instance, in cases of the impeachment of the President (Article 61) and the dismissal of judges, the legislature performs the judicial duty.
- powers, privileges, and immunities of the executives under Article 105.
- The executive head must follow the guidance and recommendations of the cabinet, according to Article 74(1).
- The Court has the authority to review any constitutional amendments made by parliament.
Concerns Regarding Functional Overlapping
- Accountability: One drawback of overlapping powers is that one organ cannot be held responsible for its actions. For instance, judicial decisions in the allocation cases for 2G and coal.
- Faith can be eroded by repeatedly interfering with one organ’s ability to function in a way that is detrimental to the integrity, effectiveness, and quality of the other organs.
- Accumulation of power: It erodes the spirit of democracy because it weakens the check and balance system when too much power is concentrated in certain political institutions.
- Negative impact on development: Overstepping one jurisdiction’s boundaries may make it difficult for the government to run effectively, harming both public services and overall development.
Significance of functional overlapping
- Governmental bodies have the authority to stop arbitrary actions by the other two bodies as a check and balance. For instance, the Supreme Court’s authority to conduct judicial review
- Rule of law: Power-sharing agreements between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government improve accountability and equity in rule of law.
- Reduces scope of dispute among government organs: The constitutional separation of the supreme and subordinate powers limits arbitrary behavior.
- Cooperation: Overlapping functions lead to power decentralization and sharing.
Judicial overreach and Judicial Activism
- Judicial activism is the term for the judiciary’s proactive role in advancing justice in society and defending the rights of citizens.
- When the court begins to interfere with how the legislative or executive branches of the government conduct their business, that is what is known as judicial overreach.
- Both judicial activism and judicial excess violate the separation of powers, such as when they interfere with the executive’s daily operations or make laws or frame policies.
- It talks about the executive’s and legislature’s inaction.
- creates a judiciary that is active and pro-people. At the same time, it undermines democracy’s spirit.
- Suo Moto lawsuits and Public Interest Litigation (PIL) have made it possible for the judiciary to get involved in numerous public matters even when the party in question hasn’t filed a complaint.
Recent Occurrences
- In Delhi, the national green tribunal has banned diesel trucks older than ten years.
- Orders on Diwali fireworks, citing increased pollution and environmental protection.
- The Pegasus case raises serious concerns about the Supreme Court and judicial independence, and it is being used to invalidate the National Judicial Accountability Commission Act, which seeks to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Decriminalization of Homosexuality.
- Supreme Court Instructions in the Prakash Singh Case of 2006: The Supreme Court’s seven main instructions in the judgment included establishing the tenure and choosing the DGP (Director General of Police) to prevent instances when officers who were about to retire were awarded the position.
Way Ahead
- A necessary part of the evolution of democracy is the theory of separation of powers. None of the republic’s three distinct organs may assume the duties delegated to the other.
- The executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government work together to fill the gap and ensure efficient operation.
- A Constitutional system with a tight division of powers is unwelcome and impractical for a democratic government and varied population like India. But sensible and deliberate constitutional functional overlap opens the door to democratic cooperation between the three branches of the government.
- Such shared cooperation fills the gap between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government, promoting efficient operation.
Source:
Download the PDF Now:
Plutus IAS current affairs 11th Jan 2023
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
UPSC aspirants should enhance their general knowledge to pass the UPSC exam. Daily Current Affairs play a vital role in increasing the general knowledge that helps them prepare for UPSC Examination. Here, Plutus IAS delivers the best daily current Affairs for the UPSC examination free of cost.
Also, get weekly, and monthly current affairs for your IAS examination.




No Comments