24 Jul Ricardian Theory of Distribution
Ricardian Theory of Distribution – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Introduction
The theory of distribution deals with the functional distribution of national income among the factors of production—land, labor, and capital. One of the most significant classical contributions to this field is from David Ricardo, whose Ricardian Theory of Distribution emphasizes the role of land fertility and diminishing returns in determining rent, wages, and profit. This theory is foundational to classical economics and remains a crucial topic in the UPSC Economics optional syllabus.
1. Overview of Ricardian Distribution Theory
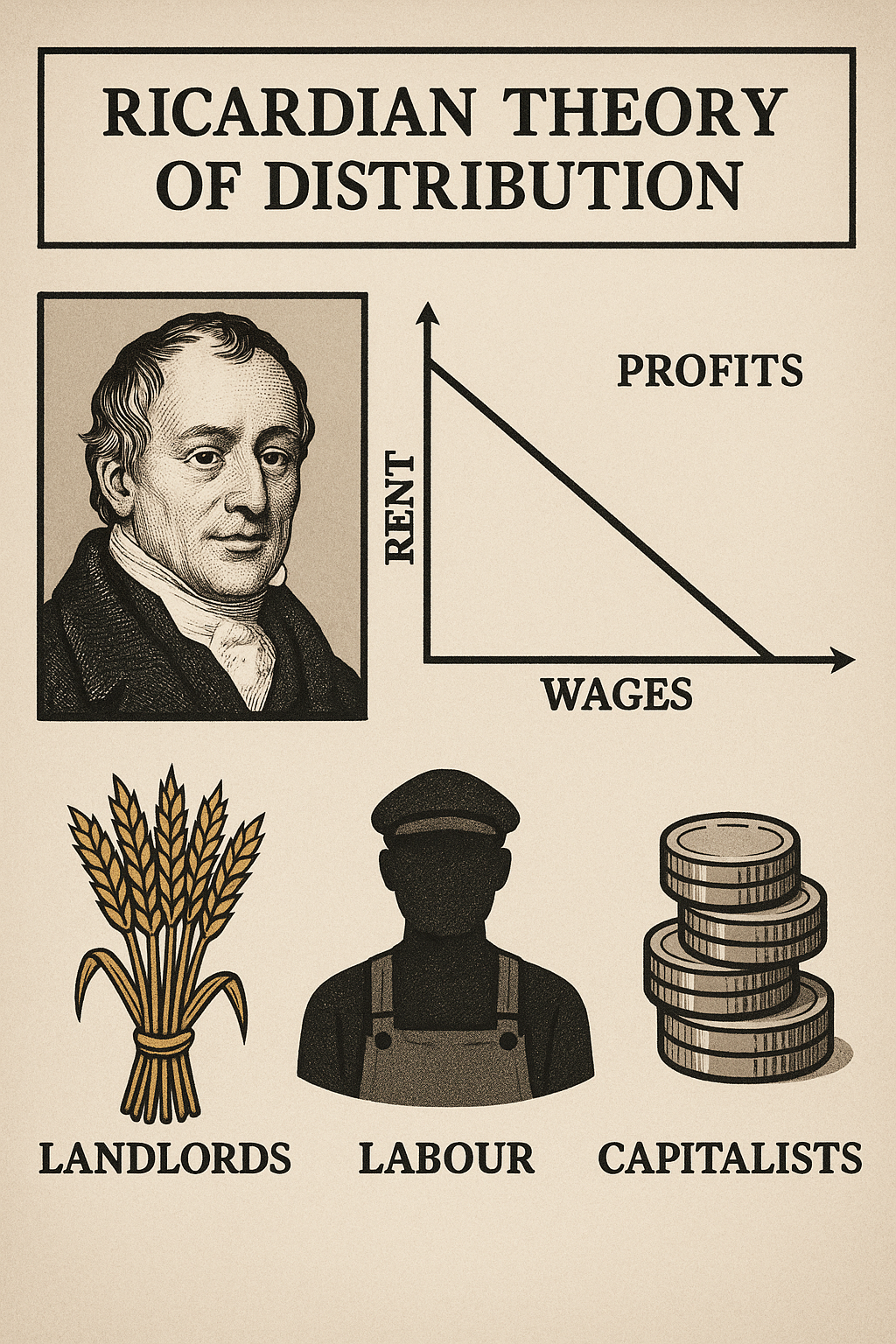
David Ricardo’s theory is based on a three-class economy:
- Landlords: earn rent
- Workers: earn wages
- Capitalists: earn profits
Ricardo assumed that land was heterogeneous in fertility and that agriculture was subject to the law of diminishing returns. He used these premises to explain how rent, wages, and profits interact over time.
best economics optional test series
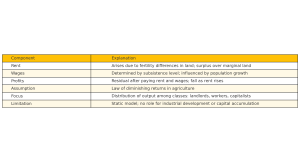
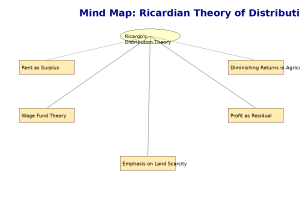
2. Theory of Rent
Ricardo defined rent as the payment made for the use of the “original and indestructible powers of the soil.” According to him:
- Rent arises only when land of varying fertility is brought under cultivation.
- It is the difference between the produce of superior land and that of the marginal land (no-rent land).
This differential rent is earned by landlords and increases with population growth and agricultural expansion.
3. Theory of Wages
Ricardo believed in the classical “subsistence wage” theory:
- Wages tend to settle at the minimum level necessary for the subsistence of workers.
- If wages rise above subsistence, population increases; if they fall below, population decreases.
- This self-regulating mechanism keeps wages near subsistence in the long run.
4. Theory of Profits
Profits are the residual left after paying rent and wages:
- As population increases, inferior land is brought into use, increasing rents.
- Higher food prices raise wages (to maintain real wages), which reduces profits.
- Thus, profits tend to decline over time as rent and wages rise.
This view led Ricardo to predict a stationary state in the economy, where profits vanish and growth halts.
5. Key Assumptions of Ricardo’s Theory
- Diminishing returns in agriculture
- Fixed supply of land
- Population grows in response to wages
- Land differs in fertility and location
- Wages determined by subsistence level
6. Strengths of Ricardian Theory
- First comprehensive and systematic theory of income distribution
- Clear understanding of how land scarcity affects income shares
- Insightful use of differential rent concept
7. Criticisms of Ricardian Distribution Theory
- Neglects role of demand in determining value
- Ignores impact of technological progress on productivity
- Overemphasis on agriculture over industry
- Rigid assumption of subsistence wages and declining profits
- No recognition of institutional or policy interventions
8. Ricardian Distribution Theory in Modern Context
Though Ricardo’s theory is outdated in its assumptions, it remains important for:
- Understanding classical political economy
- Analyzing land markets and rent determination
- Exploring inequality in agricultural societies
It has also inspired later economists like Marx and Sraffa in their distributional frameworks.
9. Infographic
Ricardian_Theory_Distribution_Infographic
10. Mind Map
Ricardian_Theory_Distribution_Mind Map
11. Previous Year UPSC Questions (Economics Optional)
- UPSC 2022: Critically examine Ricardo’s theory of rent and its implications on distribution.
- UPSC 2019: Discuss the classical view of distribution with reference to Ricardo.
- UPSC 2015: Why did Ricardo believe profits would decline in the long run?
12. Probable Questions for UPSC 2025
- Mains: “Explain Ricardo’s view on the conflict between wages and profits in the long-run.”
- Mains: “How does the Ricardian theory of rent relate to inequality in rural economies?”
- Prelims: “According to Ricardo, rent arises due to…”
- Prelims: “Which of the following is not a feature of Ricardo’s theory of distribution?”
13. Conclusion
Ricardo’s theory of distribution provides one of the earliest and most coherent frameworks for understanding how income is divided among social classes. Despite its limitations, it laid the foundation for future debates on inequality, rent, and class conflict. For UPSC aspirants with Economics optional, this theory is not just historically significant but analytically vital for mastering Paper 1.
Best economics services coaching
GS paper 4 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 3 syllabus and study plan




No Comments