India, with over 936 million internet subscribers as of December 2023 (TRAI), has become one of the most digitally connected nations globally. This rapid digital transformation has led to a surge in online financial transactions, e-governance services, and digital education, giving rise to a new class of ‘Digital Nagriks’. However, this expansion has also increased the risk of cyber threats, data breaches, and online frauds. In response, the Government of India is actively strengthening cybersecurity frameworks and digital safety measures to ensure a secure and resilient cyberspace for all citizens.
Understanding CERT-In
Established as the national agency for incident response under Section 70B of the Information Technology Act, 2000, the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) plays an imperative role in safeguarding India’s cyber landscape. Operating a 24×7 incident response Help Desk, CERT-In ensures timely responses to reported cybersecurity incidents. The organization offers comprehensive Incident Prevention and Response services alongside Security Quality Management Services to enhance cybersecurity measures across the nation.
The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) has registered several cases of cybercrimes during the last three years. The details are as follows.
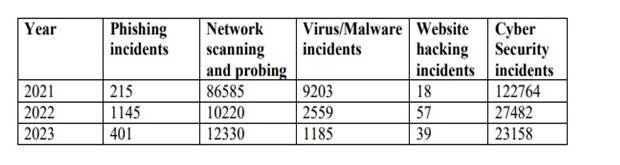
CERT-In’s efforts to combat cybercrime
1. CERT-In collaborates with service providers, regulators, and Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) to track and disable phishing websites and investigate fraudulent activities.
2. CERT-In issues advisory to Ministries outlining measures to strengthen cybersecurity for entities handling digital personal data, including sensitive information.
3. CERT-In issues advisories through RBI for audits and implementation of security practices by entities issuing prepaid payment instruments.
4. CERT-In operates an automated cyber threat exchange platform for sharing tailored alerts across sectors.
5. CERT-In manages the Cyber Swachhta Kendra for detecting and removing malicious programs, providing cyber security tips.
6. The platform has formulated a Cyber Crisis Management Plan for countering cyber attacks across government and critical sectors.
7. CERT-In conducts cybersecurity mock drills to assess readiness of organisations; 92 drills conducted with participation from diverse sectors.
8. CERT-In conducts training and workshops on specialized cybersecurity topics and offers a self-paced Cyber Security Foundation Course in collaboration with National Institute of Securities Markets and C-DAC.

Government Initiatives to Enhance Cybersecurity Awareness
1. Cyber Crime Coordination Centre: The Indian Government has established the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (14C) to enhance the coordinated response of law enforcement agencies (LEAs) to cybercrimes. This initiative aims to provide a cohesive framework for addressing digital threats comprehensively. Concurrently, the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal (https://cybercrime.gov.in) has been launched, enabling the public to report cybercrimes directly. Notably, incidents reported through this portal are automatically routed to the respective State/UT law enforcement agencies for prompt and efficient handling by legal provisions. These efforts underscore the government’s commitment to bolstering cybersecurity and empowering citizens to contribute actively to cybercrime prevention.

2. Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System: The Government launched the ‘Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System’ to facilitate the immediate reporting of financial frauds and prevent fund siphoning by fraudsters. A toll-free helpline number, ‘1930’, has been operationalized to assist with lodging online cyber complaints, ensuring swift response and support for victims of cyber fraud.
3. Multifaceted awareness campaigns: The Central Government has implemented a multifaceted approach to enhance the response to cybercrimes comprehensively. This includes extensive awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public and stakeholders about cyber threats, issuing regular alerts and advisories to highlight emerging risks, conducting specialized capacity-building and training programs for law enforcement personnel, prosecutors, and judicial officers, and improving cyber forensic facilities to bolster investigative capabilities. These initiatives collectively strengthen the government’s framework for addressing cybercrimes in a coordinated manner across the country.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act: Protecting citizen rights
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 aims to protect individuals’ rights by setting out clear principles for the lawful and transparent handling of personal data. It marks a significant step towards ensuring data privacy and building a secure digital ecosystem in India.
Key Principles of the Act:
1. Informed Consent: Data can only be processed with the prior consent of the individual (data principal), ensuring transparency and legality.
2. Purpose Limitation: Data must be used only for the specific purposes for which consent was obtained.
3. Data Minimisation: Only necessary personal data should be collected, avoiding excessive data gathering.
4. Data Accuracy: The data fiduciary is responsible for keeping personal data accurate and updated.
5. Storage Limitation: Personal data should not be retained beyond the required period for its intended use.
6. Security Safeguards: Robust technical and organizational measures must be in place to prevent data breaches and unauthorised access.
7. Accountability: Entities must comply with the Act and are liable for penalties in cases of non-compliance or data breaches.
Way Forward
1. Strengthen Data Security Measures: With rapid digital expansion, India must continuously upgrade its cybersecurity infrastructure to protect personal data from breaches and misuse.
2. Ensure Effective Implementation of the DPDP Act: Timely and transparent enforcement of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 is essential to uphold individual rights and build institutional accountability.
3. Promote User Awareness and Digital Literacy: Citizens should be educated about their data rights, the importance of consent, and how to safeguard their digital information.
4. Foster Institutional Capacity and Compliance: Public and private entities must develop strong data governance frameworks and adhere to the Act’s principles of lawful, fair, and transparent data use.
5. Encourage Technological Innovation for Data Protection: Adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies like data anonymization, encryption, and AI-driven monitoring tools will aid in secure data handling.
6. Enhance Cross-Border Data Governance: India must engage in global discussions and frameworks for secure and ethical international data transfers while protecting national interests.
7. Build Public Trust in the Digital Economy: Robust data protection laws, when effectively enforced, will boost user confidence and ensure the long-term sustainability of India’s digital growth.
Conclusion
India’s digital revolution has created new economic and governance opportunities but also introduced complex cybersecurity and privacy challenges. Institutions like CERT-In, the establishment of I4C, and the enactment of the DPDP Act, 2023 demonstrate India’s commitment to building a secure, inclusive, and rights-based digital environment. Going forward, sustained focus on awareness, enforcement, innovation, and cooperation will be essential to safeguarding the interests of Digital Nagriks and ensuring cyber sovereignty in a data-driven world.







No Comments