26 Sep Safeguarding Our Oceans: The BBNJ Agreement’s Role in Marine Pollution Containment in High Seas and Biodiversity Conservation
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and topic details of the Safeguarding Our Oceans: The BBNJ Agreement’s Role in Marine Pollution Containment in High Seas and Biodiversity Conservation.
Syllabus mapping:
GS-3: Environment and Ecology: Water pollution beyond the national borders. Marine biodiversity protection.
For Prelims:
What is Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Agreement: key facts. What are the high seas? What are India’s policies to protect the high sea and marine pollution?
For Mains:
What are the key provisions of the agreement and its implications? Significance, challenges, and implementation of the agreement signing for India?
Why in the News?
India has signed the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Agreement (BBNJ) to safeguard marine biodiversity in international waters.

Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Agreement To Protect Marine Biodiversity on High Seas

Key FACTS:
Adoption: The BBNJ Agreement was adopted on June 19, 2023, during the Intergovernmental Conference convened under the United Nations.
Context: It is the third implementing agreement of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
Institutional Arrangements: Creation of a Conference of the Parties. Establishment of subsidiary bodies, a clearinghouse mechanism, and a secretariat.
Exception: The Agreement excludes warships, military aircraft, and naval auxiliaries from its scope. The BBNJ excludes countries’ marine areas like territorial seas and exclusive economic zones (EEZs).
Nature: The BBNJ agreement is the binding agreement on the signing members.
India: India has signed the agreement but is yet to ratify it.
UNCLOS:
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) is the UN treaty regulating the international waters
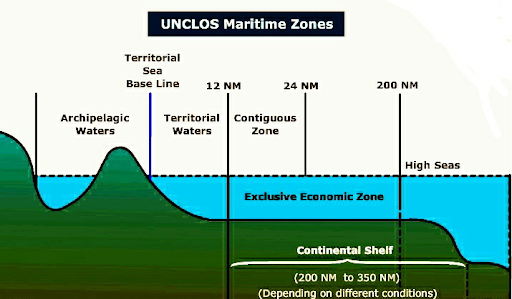
Objectives of the BBNJ Agreement
1. Conservation and Sustainable Use: Conserve and sustainably use marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction through effective implementation and international cooperation.
2. Fair Sharing of Marine Genetic Resources: Ensure fair and equitable sharing of benefits derived from marine genetic resources.
3. Area-Based Management: Implement area-based management measures, including marine protected areas, to safeguard critical ecosystems.
4. Environmental Impact Assessments: Establish procedures for conducting environmental impact assessments of activities affecting the marine environment.
5. Capacity-Building and Technology Transfer: Promote the transfer of marine technology and enhance capacities, especially for developing countries.
6. Addressing Cross-Cutting Issues: Tackle interconnected issues through a comprehensive approach, including establishing a funding mechanism for implementation.
Key Principles Under BBNJ
1. Polluter-Pays Principle
2. Common Heritage of Humankind
3. Freedom of Marine Scientific Research
4. Equity and Fair Benefit Sharing
5. Precautionary Principle
6. Ecosystem Approach
7. Integrated Ocean Management
8. Traditional Knowledge
9. Respect for Indigenous Rights
10. Non-Transfer of Pollution
Significance of the BBNJ Agreement
Legal Framework: Reinforces UNCLOS obligations to protect and preserve the marine environment.
Addressing Biodiversity Loss: Urgently tackles biodiversity loss and marine ecosystem degradation amid climate challenges.
Comprehensive Global Regime: Establishes a vital framework for conserving marine biological diversity beyond national jurisdiction.
Promoting a Fair Economic Order: Advocates for a just international economic order that meets the needs of all states, especially developing ones.
Capacity-Building Support: Emphasizes the importance of capacity-building and technology transfer for developing states.
Protection of Indigenous Rights: Affirms the rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities, aligning with international standards.
Environmental Impact Assessments: Mandates environmental impact assessments for activities under state jurisdiction.
Pollution Prevention: Recognizes states’ responsibility to prevent pollution from spreading beyond their sovereign rights.
Ocean Stewardship: Commits to responsible ocean stewardship for the protection of marine environments for future generations.
Access to Digital Sequence Information: Highlights the significance of accessing and utilizing digital sequence information on marine genetic resources.
Implications for India
Enhanced Global Standing: Positions India as a leader in marine conservation, boosting its international reputation.
Conservation of Marine Biodiversity: Supports sustainable use of marine resources, aligning with India’s biodiversity protection goals.
Economic Opportunities: Facilitates participation in the sharing of marine genetic resources, fostering economic growth and innovation in biotechnology.
Support for Coastal and Island Communities: Acknowledges Indigenous rights, aiding India’s integration of local communities in conservation efforts.
Capacity Building and Technology Transfer: Provides access to initiatives that enhance India’s marine resource management capabilities.
Strengthened Regional Cooperation: Encourages collaboration with neighboring countries on marine conservation, particularly in the Indian Ocean.
Addressing Climate Change: Aligns with India’s climate action goals by promoting ecosystem resilience against climate impacts.
Potential Economic Costs: Involves financial implications for implementation, including monitoring and capacity-building efforts.
Challenges of the BBNJ Agreement
Resource Regulation Conflicts: The focus on living resources may conflict with states’ economic interests in non-living resources like oil and gas.
Infringement on State Rights: Marine-protected areas could restrict states’ freedoms on the high seas, raising sovereignty concerns.
Tension Between the Area and Extended Continental Shelf: Uncertainty about the BENJI’s scope until continental shelf limits are defined may delay implementation.
Historical Resistance from Industrialized States: Provisions for technology transfer and financial contributions may face pushback from industrialized nations.
Equitable Sharing of Benefits and Technology Transfer: Requirements for equitable sharing of benefits and technology transfer may hinder compliance and create tensions among states.
Way Forward
International Collaboration: Strengthen global cooperation to effectively implement the BBNJ Agreement.
Leadership Role of India: Position India as a leader in marine conservation and sustainable use efforts.
Financial Assistance from Developed Countries: Secure funding and support from developed nations to aid implementation.
Engagement of Major Polluters: Encourage major polluters like China and the US to sign and commit to the Agreement.
Protection of Indigenous Rights: Ensure the rights of Indigenous Peoples are respected and integrated into conservation strategies.
Phased Implementation: Adopt a phased approach to implementation, allowing for gradual adjustment and capacity-building.
Review and Stocktake: Establish regular review mechanisms, similar to the Paris Agreement, to assess progress and adapt strategies.
Building Trust: Foster mutual trust among nations to enhance cooperation and commitment to conservation efforts.
Conclusion:
The BBNJ treaty marks a significant advancement in international law by regulating activities on the high seas directly, addressing gaps in UNCLOS to enhance environmental protection. However, it also inherits challenges that could hinder cooperation and compliance. As the treaty undergoes harmonization, it is crucial to address these issues to promote effective implementation and ensure the safeguarding of marine ecosystems.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 26th Sep 2024
Prelims Question:
Q.With reference to the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Agreement (BBNJ), Consider the following statement:
1. The BBNJ agreement is aimed at reducing marine pollution in all seawaters.
2. The BBNJ Agreement applies to commercial and military ships.
3. India has recently rectified the BBNJ agreement.
4. The BBNJ agreement is based on the polluter pay principle.
How many of the above-given statements are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. Only three
D. All four
ANSWER: A
Mains Question:
The Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Agreement (BBNJ) is a milestone agreement in the history of marine protection and the need is to act collectively to make smooth implementation of the BBNJ agreement. Elaborate.
(Answer in 250 words)




No Comments