06 Aug SEMICON India 2025: Showcasing Strength in Semiconductor Ecosystem
Posted at 06 Aug 2025
in
Current Affairs
by Ritik singh
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the Topic SEMICON India 2025: Showcasing Strength in Semiconductor Ecosystem
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-3-Science and technology- SEMICON India 2025: Showcasing Strength in Semiconductor Ecosystem
FOR PRELIMS
Why are semiconductors crucial to India’s digital economy and national security?
FOR MAINS
What are the major features of SEMICON India 2025?
Why in the News?
Semiconductors have recently gained national and global attention due to their critical role in powering modern technologies—from smartphones and computers to satellites and defence systems. With India’s push for self-reliance under the Semiconductor Mission and the successful use of indigenous semiconductor-based technology in missions like Chandrayaan-3, where the Vikram lander used Indian-made chips and AI for autonomous landing, the spotlight is back on this tiny yet powerful innovation shaping the future of digital infrastructure and strategic capabilities.
“Today’s India inspires confidence in the world… When the chips are down, you can bet on India”– Prime Minister Narendra Modi.

These chips are therefore the backbone of modern electronics, enabling the functioning of devices such as smartphones, computers, electric vehicles, satellites and even defence systems like Aaksh teer.
The chips are made from semiconductor material and can store, process, and transfer information, helping devices perform tasks such as calling, storing data, or sensing electrical signals. Each chip contains millions (or even billions) of microscale switches called transistors, which control electrical signals much like brain cells pass messages in our bodies. It also has other tiny components like resistors, capacitors, and wiring. Together, these elements process and move information.
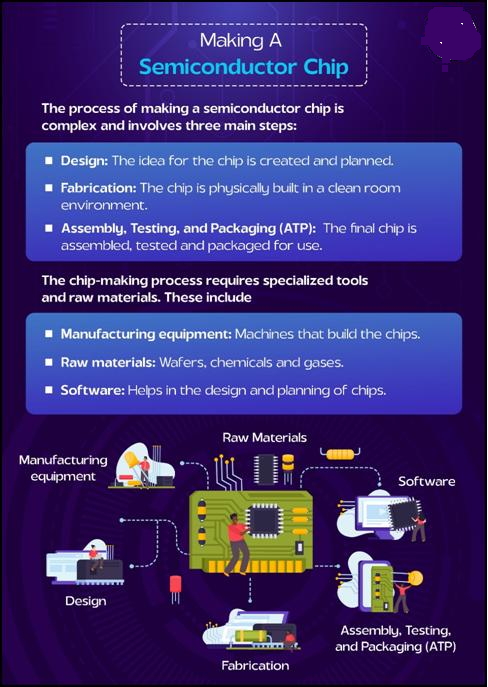
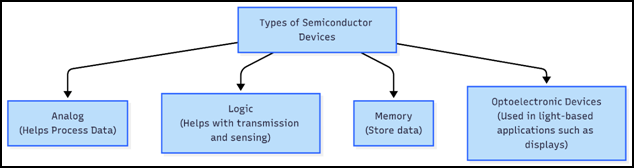
Why Semiconductor Industry Matters: A Strategic Context
Semiconductors are the foundation of modern technology, powering key sectors like healthcare, transport, communication, defence, and space. As digitalisation and automation accelerate, these chips have become vital for economic resilience and strategic autonomy. The global chip shortage post-COVID-19 and the Russia-Ukraine war exposed vulnerabilities in supply chains, disrupting industries worldwide. Rising demand for faster, efficient, and compact chips is driven by growing digitisation, smart devices, AI, and cloud computing. Semiconductors now enable real-time data processing and decision-making across systems. Currently, the industry is dominated by a few nations—Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, China, and the U.S.—with Taiwan alone producing over 60% of global chips and nearly 90% of advanced ones. This dependence has raised concerns over supply chain risks, prompting countries like the U.S., EU, and Japan to boost domestic manufacturing. India is emerging as a key player in this global shift. Through the India Semiconductor Mission, PLI schemes, and global partnerships, it aims to build a strong semiconductor ecosystem. With its growing digital economy and skilled workforce, India is well-positioned to become a trusted and strategic hub in the evolving global semiconductor landscape.

India as a player in the Semiconductor Market
With global chip demand rising and supply chains vulnerable due to geographic concentration, India is positioning itself as a key player in diversifying semiconductor manufacturing. Strategic initiatives like including Electronics Systems Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) under Make in India, along with the India Semiconductor Mission and Semicon India programme, have laid the foundation for a robust domestic ecosystem.
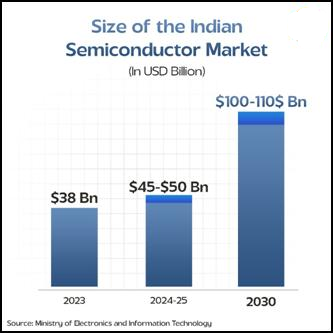
The global semiconductor market is projected to reach USD 1 trillion by 2030, with India expected to claim a significant share. India has the potential to contribute across the three core pillars of the semiconductor supply chain:
Equipment – leveraging a strong MSME base to manufacture critical components;
Materials – being rich in essential chemicals, minerals, and gases;
Services – offering advanced capabilities in R&D, logistics, and a skilled talent pool in AI, cloud computing, IoT, and big data.
In May 2025, the Union Minister for Electronics & IT, Railways, and Information & Broadcasting, Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, inaugurated two state-of-the-art semiconductor design facilities in Noida and Bengaluru. These centres are India’s first to focus on advanced 3-nanometer chip design, marking a significant milestone in the nation’s semiconductor innovation journey.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
Launched in December 2021 with a ₹76,000 crore outlay, the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) aims to boost domestic capabilities in chip fabrication, display manufacturing, and design. It seeks to position India as a global hub for electronics manufacturing by integrating into global value chains. Led by industry experts, ISM serves as the nodal agency for implementing semiconductor and display schemes, fostering a robust and self-reliant ecosystem.
Mission focus of ISM
Set up Chip Manufacturing plants(fabs)
Create packaging and testing units
Supporting startups in chip design
Training young engineers
Bring Global companies to invest in India
Objectives of the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
1. Ecosystem Development: Create a long-term strategy for sustainable semiconductor and display manufacturing and design in India.
2. Secure Supply Chain: Develop a trusted and secure semiconductor supply chain, including raw materials, chemicals, gases, and equipment.
3. Support for Design Start-ups: Boost the semiconductor design industry by providing EDA tools, foundry access, and early-stage support.
4. Indigenous IP Generation: Promote the creation of domestic intellectual property in semiconductors and displays.
5. Technology Transfer (ToT): Encourage and facilitate transfer of advanced technologies to India.
6. Economies of Scale: Establish mechanisms to scale manufacturing and reduce costs.
7. Advanced R&D: Support cutting-edge research through grants, Centres of Excellence, and global collaborations.
8. Collaborations & Skill Development: Foster national and international partnerships for research, commercialization, and workforce training.

Key Schemes under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
1. Semiconductor Fabs Scheme: Up to 50% fiscal support for setting up semiconductor fabs targeting 28nm and mature nodes. Aims to meet domestic and global chip demand.
2. Display Fabs Scheme: Provides up to 50% support for AMOLED and LCD display units. Seeks to reduce imports and boost local display manufacturing.
3. Compound Semiconductors & ATMP/OSAT Scheme: Supports units for compound semiconductors, MEMS, and chip packaging/testing (ATMP/OSAT) with up to 50% funding. Strengthens the full semiconductor value chain.
4. Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme: ₹1000 crore outlay to support design startups and MSMEs. Offers R&D reimbursement, design tool access, and up to ₹15 crore per company.
₹234 crore already committed to 22 startups for chip designs in sectors like CCTV, telecom, satellites, and automobiles.
Strategic Collaborations under ISM
1. Lam Research & IISc: MoU to train 60,000 engineers using the Semiverse simulation platform over the next decade.
2. Future Skills Program: Government initiative to train 20,000 engineers in Madhya Pradesh in semiconductor-related skills.
3. Micron & IIT Roorkee: Partnership to promote innovation and develop a skilled workforce in chip design and manufacturing.
4. IBM Collaboration: Offers Indian students and professionals access to advanced labs, internships, and research centres to enhance industry-aligned skills.
5. Purdue University: MoU for collaborative R&D, talent development, and commercialization in semiconductors and display technologies, bridging academia and industry.
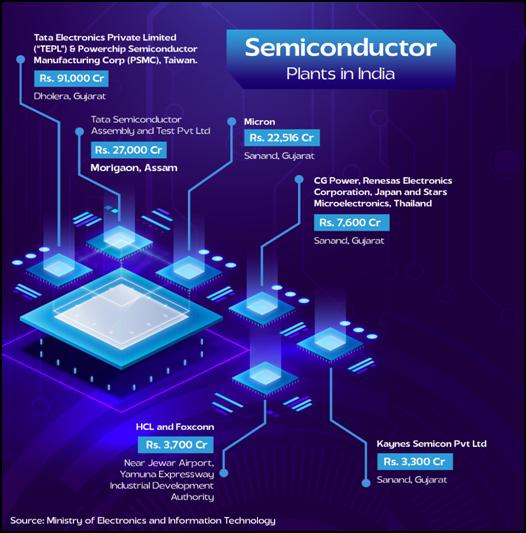
Mapping India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem
| Date |
Company |
Location |
Investment |
Output Capacity |
| Jun 2023 |
Micron Technology |
Sanand, Gujarat |
₹22,516 crore |
ATMP Facility (phased ramp-up) |
| Feb 2024 |
Tata Electronics (TEPL) & PSMC (Taiwan) |
Dholera, Gujarat |
~₹91,000 crore |
50,000 wafers/month |
| Feb 2024 |
CG Power & Industrial with Renesas & Stars |
Sanand, Gujarat |
~₹7,600 crore |
15 million chips/day |
| Feb 2024 |
Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test (TSAT) |
Morigaon, Assam |
₹27,000 crore |
48 million chips/day |
| Sept 2024 |
Kaynes Semicon Pvt Ltd |
Sanand, Gujarat |
₹3,307 crore |
6.33 million chips/day |
| May 2025 |
HCL-Foxconn Joint Venture |
Jewar, Uttar Pradesh |
₹3,700 crore |
20,000 wafers/month (36 million units/year) |
SEMICON India: Showcasing India’s Semiconductor Leadership
As part of its ₹76,000 crore India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), the government launched SEMICON India, a flagship initiative to position India as a global semiconductor hub. Organized in partnership with SEMI (Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International), the platform brings together global industry leaders, policymakers, academia, and startups to foster investment, innovation, and strategic collaboration.
SEMICON India 2025 Features:
1. Record stakeholder participation across the supply chain
2. First-ever Global Pavilions, Country Roundtables, and Design Startup Pavilion
3. Major focus on Skilling Initiatives and Research Commercialization
4. Over 300 exhibiting companies from 18 countries and regions
5. Targeted at business leaders, innovators, researchers, engineers, students, and industry professionals
6. SEMICON India plays a crucial role in advancing India’s semiconductor ambitions through global partnerships, Skill development, and innovation promotion.
Key Features of SEMICON India 2025
1. Wider Stakeholder Participation: With over 300 exhibitors from 18 countries, this edition marks a major leap in global engagement, reflecting India’s growing stature in the semiconductor ecosystem.
2. International Pavilions: For the first time, four country pavilions—Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and Malaysia—will showcase their capabilities and foster partnerships.
3. Country Roundtables: Eight high-level roundtables will facilitate strategic dialogue between government, industry leaders, and companies from India and partner nations.
4. Workforce Development Pavilion: With the sector projected to need 1 million skilled professionals by 2030, this pavilion will focus on career counselling, skilling, and mentoring for students and engineers.
5. Semiconductor Design Startup Pavilion: A dedicated space to promote chip design startups, alongside participation from nine state governments, up from six last year.
6. Additional Features: Includes Startup Pavilion, B2B forums, and initiatives to strengthen India’s talent pipeline and innovation ecosystem.
Conclusion
India’s electronic industry is growing rapidly, with semiconductors at the heart of this transformation. To meet rising demand and reduce import dependence, the government has launched strategic initiatives like the India Semiconductor Mission, the SEMICON India Programme, and global partnerships such as iCET. These efforts signal India’s shift from a consumer to a key player in the global semiconductor value chain. As approved facilities begin operations and new projects take shape, the country is positioning itself as a trusted hub for semiconductor manufacturing, strengthening its digital economy, national security, and technological self-reliance. From dependence to dominance, the chip revolution is real and its happening right here, right now in Bharat.
Prelims Questions
Q. SEMICON India 2025 will feature international pavilions from which of the following countries?
1. Japan
2. Taiwan
3. South Korea
4. Malaysia
5. Singapore
Select the correct option:
A) 1, 2, 3 and 5
B) 1, 3, 4 and 5
C) 2, 3, 4 and 5
D) 1, 2, 4 and 5
Answer: B
Mains Questions
Q. India is shifting from dependence to dominance in the semiconductor industry. Discuss the role of the India Semiconductor Mission and initiatives like SEMICON India in driving this transformation.
(250 words, 15 marks)











No Comments