08 Jul Smart Cities Mission Extension till March 2025
(This article is from the section ‘ Indian Constitution and Governance, Smart Cities Mission: Significance and Challenges, Urbanisation, Social Empowerment’ of UPSC Civil Services Mains General Studies Paper- 2 and ‘ Smart Cities Mission, Sustainable Development, Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), Public-Private Partnership (PPP), Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) ’ of UPSC Prelims Exam. It also includes suggestions from the PLUTUS IAS Team. This article is from ‘ Smart Cities Mission Extension till March 2025 ’ of ‘ Daily Current Affairs’.)
Why in the NEWS ?

- The Central Government has recently extended the deadline of the Smart City Mission again.
- Now the target has been set to complete this mission by March 31, 2025.
- This mission was launched with the aim of promoting urban development of India and its main objective is to improve cities through technological and digital solutions.
- Under this mission, 100 cities have developed various projects. These projects have improved the capacity and experience of cities and achieved major transformational goals at the city level.
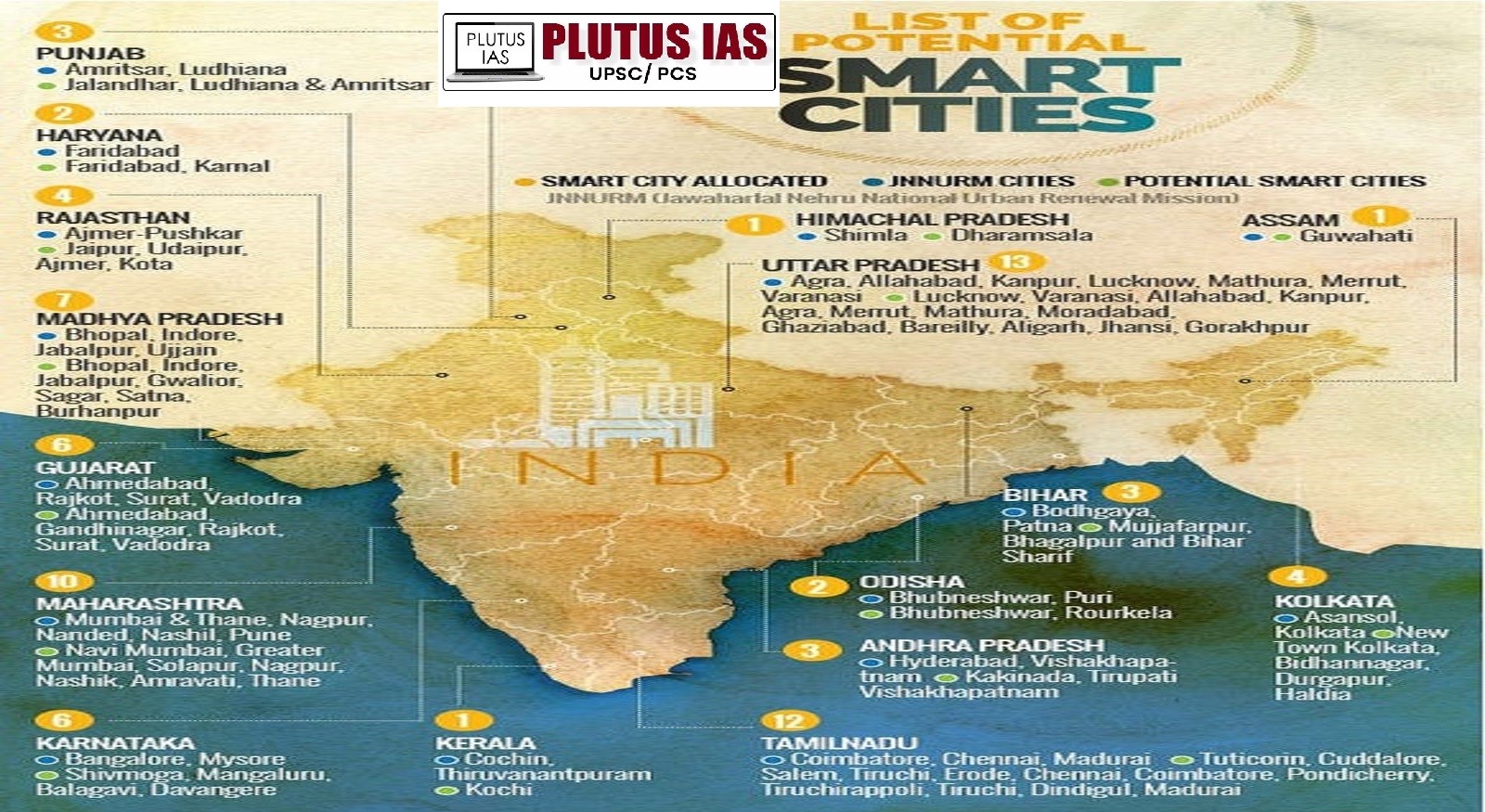
What is a Smart city?
- Smart city is a concept that refers to the use of technology, data and innovative solutions to improve efficiency, sustainability as well as quality of life in urban areas.
- Its core infrastructure includes water supply, power supply, solid waste management, sanitation, efficient urban mobility, public transport, affordable housing, IT connectivity, digitalization, good governance, e-governance, citizen participation, environmental sustainability, and safety of citizens. .
- According to the census of 2011About 31% of India’s current population lives in cities and their contribution to the gross domestic product (GDP) is 63%.
- It is estimated that by the year 2030, 40% of India’s population will live in urban areas and their contribution to India’s GDP will be 75%.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM) :
- Smart Cities Mission (SCM) It is a scheme launched by the Government of India to improve the quality of life of citizens living in cities and towns across the country.
- It was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 25 June 2015.
- This The objective of the scheme is to develop infrastructure to provide a clean and sustainable environment to the citizens.
Main components of SCM :
Following are the main components of Smart Cities Mission (SCM) –
Area-based development :
Redevelopment (city renewal) : Renovation of existing urban areas to improve infrastructure and facilities.
Retrofitting (city improvement) : To develop infrastructure to make existing areas more useful and sustainable.
Greenfield Projects (City Expansion) : new with a focus on sustainability and smart technologies To develop urban areas.
Pan – City Solution :
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) solutions are applied in various sectors like e-governance, waste management, water management, energy management, urban mobility and skill development.
Governance Structure :
- To adopt the new governance model, a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) was created under the Companies Act, 2013, which will be led by bureaucrats or multinational corporations (MNCs). It was done by representatives of. To increase its effectiveness, a new governance model was adopted.
Financing Smart Cities :
- About Rs 48,000 crore (an average of Rs 100 crore per city per year) provided by the Central Government for five years for SCM plays a vital role in the development of these cities.
- States and urban local bodies (ULBs) are also required to contribute an equal amount, taking the total amount to around Rs 1 lakh crore.
Benefits to be derived from convergence with other government schemes :
- Linking the resources and objectives of SCM with schemes like AMRUT (Urban Transformation), Swachh Bharat Mission (Sanitation), HRIDAY (Heritage City Development), Digital India, Skill Development, and Housing for All increases its effectiveness.
- Under SCM, existing funds and infrastructure of various schemes can be leveraged in order to achieve common goals.
- Its convergence with other schemes ensures that along with the development of physical infrastructure, social infrastructure (health, education, culture) is also given prominence in smart cities.
- SCM can be strategically integrated with other programs of the Central and State Government to harness its full potential.
Challenges before Smart City Mission :
Following are the important challenges before the successful implementation of Smart City Mission (SCM) –
- Delay in completion of project : About 10% of the projects under this scheme are still incomplete, which is an indication of delay in the execution of this project. The reasons behind this could be lack of technical expertise, land acquisition problems and other problems.
- lack of financing : 26 cities in India have still not received the full financial amount, while 74 cities have received 100% of their central share.
- Challenges of SPV Model : The Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) model adopted for smart city projects has faced objections due to misalignment with the constitutional amendment.
- Lack of coordination : The mutual lack of coordination between the Central, State and local governments under the scheme has hindered the smooth implementation of the mission.
- Displacement and social impact : The scheme has led to the displacement of residents from poor areas, disrupting the fabric of urban communities. Infrastructure development in some towns has contributed to an increase in urban flooding due to disruption of water systems.
Solution / Way forward :
Smart City Mission to be effective and successful Implementation The following steps can be taken for –
Effective governance and implementation of the plan :
- The appointment of CEOs with fixed tenure will ensure continuity and attract qualified professionals.
- Various stakeholders including experts and Members of Parliament (MPs) should push for inclusive decision making.
Strategic focus on the project :
- Smart City Mission (SCM) is a plan to generate and utilize large amounts of data from various sources under digital infrastructure. Therefore, these platforms must implement a robust system to protect against cyber attacks as well as ensure the security of sensitive public and private data.
Data Security and its Upgrade :
- Strong digital infrastructure must be established to counter cyber threats and protect data privacy.
- An overall operations and maintenance strategy should be developed to maximize the life of the infrastructure and ensure its timely upgrades.
Capacity building and financing :
- Urban local bodies (ULBs) in small towns should be strengthened through capacity building programmes.
- In this sequence, central government assistance for organizational restructuring and skill development can be important.
Ensuring implementation of projects :
- The role of the concerned ministry should extend from fund allocation to active monitoring and providing expertise for timely project execution.
Global Knowledge Sharing :
- Similar projects related to sustainable urban development in developing countries can be crucial for information sharing in this context.
- Bhutan’s Gelephu Smart City Project The main objective of the IFR is to create an economic corridor connecting South Asia with South East Asia, covering the north-eastern states of India. Giving priority to environmental standards and sustainability in this will attract investment from international companies.
Source – The Hindu and PIB.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 08th July 2024
Practice Questions for Preliminary Exam :
Q.1. Consider the following statements regarding Smart Cities Mission.
- The main objective of this scheme is to improve the cities of India through technical and digital means.
- According to the 2011 census, their contribution to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is 63%.
- It was launched by the Prime Minister of India in June 2015.
- This plan has led to an increase in urban flooding.
Which of the above statement / statements is/ are correct?
A. Only 1, 2 and 3.
B. Only 2, 3 and 4.
C. None of these.
D. All of the above.
Answer – D
Practice Questions for Main Exam :
Q.1. Highlighting the major provisions of the Smart Cities Mission, Discuss what are the main challenges facing the successful implementation of the Smart Cities Mission in India and how can those challenges be resolved? ( UPSC CSE – 2017 Word Limit – 250 Marks – 15 )




No Comments