16 Jan Startup India: Igniting Innovation, Empowering Entrepreneurs, Boosting the Economy”
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs,” and the topic details related to” Startup India: Igniting Innovation, Empowering Entrepreneurs, Boosting the Economy”
Syllabus mapping:
GS-3: India Economy: Various sectors of the Economy- MSME sector.
For Prelims:
What are the key features of the Start-up India Proegarmme?
For Mains:
What are startup India Initiatives, their features and challenges related to startups in India, and ways to promote the startup Culture?
Why in the news?
On January 16, 2025, India celebrated the 9th anniversary of the Startup India initiative, launched in 2016 as a flagship program of the Government of India. Designated as National Startup Day, this occasion highlights the nation’s remarkable progress in fostering a dynamic and inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
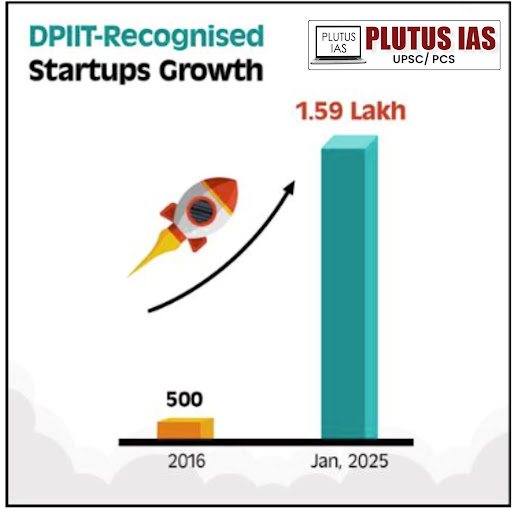
The Startup Culture in India:
DPIIT-Recognized Startups: The number of recognized startups has grown from 500 in 2016 to 1,59,157 as of January 15, 2025, reflecting a vibrant and thriving entrepreneurial culture.
Women Entrepreneurs: By October 31, 2024, 73,151 startups included at least one woman director, highlighting the rise of women entrepreneurs and their crucial role in shaping India’s startup landscape.
Job Creation: Startups have generated over 16.6 lakh direct jobs between 2016 and October 31, 2024, significantly contributing to India’s employment and economic growth.
Global Recognition: India ranks as the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world, demonstrating its prowess on the global stage.
Unicorn Boom: With over 100 unicorns, Indian startups are redefining global innovation and showcasing entrepreneurial success.
Regional Expansion: While major hubs like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, and Delhi-NCR lead the transformation, smaller cities are emerging as key contributors to India’s entrepreneurial momentum.
Sectoral Excellence: Startups in sectors like fintech, edtech, health tech, and e-commerce have addressed local challenges and earned global acclaim.
Inspiring Success Stories: Companies such as Zomato, Nykaa, and Ola embody India’s shift from a nation of job seekers to job creators, driving economic development and inspiring future entrepreneurs.
Key Facts of the Startup India Scheme:
Launched: The Startup India scheme was launched by the Government of India on January 16, 2016, to promote entrepreneurship and innovation.
Benefits: Offers tax incentives, legal support, and funding options.
Goals: Aim to reduce regulatory burden, promote innovation, and create jobs.
Eligibility: Available to startups within 10 years of incorporation.
Self-certification: Startups can self-certify compliance with certain labor and environmental laws.
Funding: Provides funding for startups, including those led by women and from SC/ST communities.
Legal Support: Offers low-cost legal assistance and fast-track patent processing.
Tax Incentives: Includes capital gains tax exemptions and other tax benefits.
Seed Fund: The Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS) provides financial assistance to early-stage startups.

Schemes and support under the Startup India initiative
Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS)

Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS)

Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme
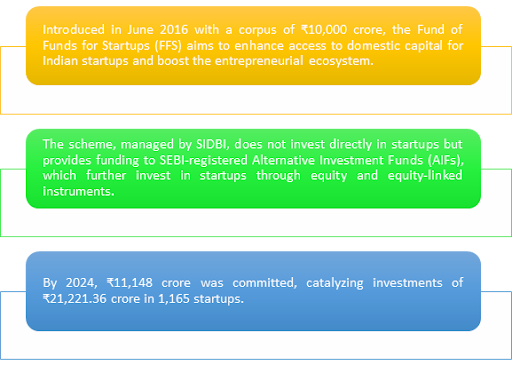
Significance of the Startup India initiative:
| Key Contribution | Details |
|---|---|
| Boosting Domestic Capital | ₹10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) launched in 2016 to enhance access to capital. |
| Innovative Funding Approach | Managed by SIDBI, funding provided through SEBI-registered Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs). |
| Significant Financial Commitment | By 2024, ₹11,148 crore committed, catalyzing investments across the startup ecosystem. |
| Economic Multiplier Effect | Investments of ₹21,221.36 crore mobilized across 1,165 startups, amplifying economic impact. |
| Employment Generation | Over 16.6 lakh direct jobs created by recognized startups from 2016 to October 31, 2024. |
| Empowering Women Entrepreneurs | 73,151 startups (as of October 31, 2024) include at least one woman director, promoting women empowerment. |
| Encouraging Entrepreneurship | Enabled startups to innovate and scale, fostering entrepreneurship as a key driver of economic growth. |
| Sector-Wide Growth | Supported startups across industries like technology, health, and finance, driving sectoral innovation. |
| Strengthening Global Position | Established India as the third-largest startup ecosystem globally, attracting international recognition. |
| Fostering Inclusive Growth | Promoted inclusivity by supporting entrepreneurs from all backgrounds, including women and non-metro regions. |
Challenges faced by startups in India:
Funding Constraints: Despite significant investments from government initiatives and venture capitalists, access to early-stage funding remains a challenge. According to NASSCOM, over 90% of startups fail due to lack of funds, especially in the first 2-3 years.
Regulatory and Compliance Burdens: A 2022 study by Deloitte found that 52% of Indian startups face challenges in regulatory compliance, especially in sectors like fintech, healthcare, and e-commerce.
Talent Acquisition and Retention: A shortage of skilled talent, particularly in emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and data science, is a major hurdle. According to the 2023 Startup Ecosystem Report, over 60% of startups cite talent acquisition as a major challenge, with high turnover rates in technical roles.
Market Access and Competition: Startups often find it difficult to access a wide customer base, competing with established industry giants. A report by McKinsey suggests that 70% of Indian startups face significant competition from well-established brands, making market entry and brand recognition a prolonged struggle.
Infrastructure and Resources: While tier-1 cities like Bengaluru and Delhi have thriving startup ecosystems, startups in smaller cities and rural areas often face limited access to essential infrastructure, technology, and mentorship. A 2021 study by the World Bank showed that 67% of Indian startups are concentrated in metro cities, leaving rural areas underserved.
Cultural Barriers: Entrepreneurship is still viewed with caution in many regions. In a 2020 survey by the Indian School of Business, 44% of respondents from non-metro areas cited societal pressures and fear of failure as major deterrents for pursuing entrepreneurship.
Access to Networks and Mentorship: Many startups in India struggle to connect with experienced mentors and investors. According to a 2021 survey by TiE Global, over 40% of entrepreneurs reported difficulty in finding industry-specific mentors or networks, limiting their ability to scale.
Lack of Effective Marketing Strategies: Many startups struggle to develop effective marketing strategies due to budget constraints and limited marketing expertise. According to a 2022 survey by KPMG, 58% of startups in India cited marketing and customer acquisition costs as one of their top challenges.
Way Forward for Startups in India:
Enhancing Access to Funding: Expand funding through angel networks, crowdfunding, and government schemes like the Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS).
Simplifying Regulations: Streamline regulatory processes and reduce delays as per the Startup India Annual Report 2023. Create a startup-friendly legal and tax environment to ease compliance burdens (DPIIT).
Fostering Corporate Collaboration: Encourage partnerships between startups and corporations for market access and resources. Develop regional incubators and accelerators to foster innovation (National Startup Advisory Council).
Building a Skilled Workforce: Align academic curriculums with industry needs and promote industry-academia partnerships. According to NASSCOM (2023), 56% of startups struggle to find the right talent, emphasizing the need for skilled training programs.
Promoting Rural and Inclusive Innovation: Strengthen infrastructure in tier-2 and tier-3 cities and support rural and women-led startups. Aligned with Atmanirbhar Bharat to promote balanced regional development.
Developing Innovation in Emerging Sectors: Focus on sectors like biotechnology, clean energy, and sustainability with dedicated policies and funding.
Supporting Sustainable Startups: Promote eco-friendly startups in clean energy and waste management through government initiatives. Foster socially responsible businesses addressing healthcare, education, and rural development (National Rural Livelihood Mission).
Conclusion
The Startup India initiative has transformed India into a global innovation hub, with over 1.59 lakh recognized startups and a growing workforce. The initiative has empowered startups across sectors, including non-metro areas through flagship schemes, capacity-building efforts, and platforms like BHASKAR. As India moves forward, the Startup India program remains crucial in driving economic growth and fostering a dynamic entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Prelims Questions:
Q. Which of the following is/are core features of the Startup India Initiative?
1. Easy of doing business
2. Tax Exemption
3. Funding Support
4. Sector Specific policies.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a). Only one
(b). Only two
(c). Only three
(d). All four
ANSWER: d
Mains question:
Q. Evaluate the impact of the Startup India Programme on fostering innovation and entrepreneurship in India.
(Answer in 150 words)



No Comments