11 Sep Transforming Rural India: The Crucial Role of Cooperatives
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and topic details of the Role of cooperatives in the rural economy.
Syllabus mapping:
GS-3: Agriculture: Role of cooperatives in rural economy.
For Prelims:
What are the constitutional provisions? International Cooperative Alliance? Key Facts Related to Cooperatives.
For Mains:
What are the features of Cooperatives in India? What are the significance of the cooperatives in the rural economy, challenges, and ways to strengthen the cooperatives?
Why in the News?
India will host the inaugural Global Cooperative Conference in New Delhi. This will be the first time in the last 130 years history of the the International Cooperative Alliance, India will host the Conference.

What are Cooperatives?
A cooperative is an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically controlled enterprise. Cooperative principles: Self-Help, Self-Responsibility, Democracy, Equality, Equity, and, Solidarity.
Constutional Provisions:Constitution (Ninety-Seventh Amendment) Act, 2011: Fundamental Right: Article 19(1)(c): Amended to include the right to form cooperative societies as a Fundamental Right Directive Principles: Article 43B: Inserted to promote the growth and development of cooperative societies, guiding state policies to support cooperative principles. Incorporation of Part IXB: Added to the Constitution, detailing the incorporation, regulation, and winding up of cooperative societies, providing a constitutional framework for their governance and legal structure. Governance of Cooperative Societies Single state: Cooperative Societies limited within one state are regulated by the respective state laws. The Maharashtra State Cooperative Societies Act, 1960. Multi-State: Cooperative societies beyond a single state are governed by Entry 44 of the Union List in the Seventh Schedule and regulated under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, of 2002. They are administered by the Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies (CRCS). The Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill, 2023: Aims to incorporate the provisions of the Ninety-Seventh Constitutional Amendment. Seeks to enhance governance, transparency, accountability, and reform the electoral process in multi-state cooperative societies. The International Cooperative Alliance (1895):
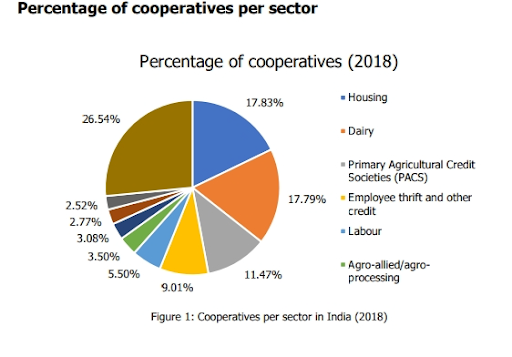
Type: One of the oldest non-governmental organizations (NGOs) Global Reach: Represents around 3 million cooperatives Membership: Approximately 1 billion cooperative members worldwide Role: Apex body for cooperatives, providing a global voice, knowledge-sharing, and coordinated action India and the ICA: The National Cooperative Union of India (NCUI) is the primary body representing Indian cooperatives within the ICA. Cooperatives scenario India:
|
Significance of the cooperatives:
1. Economic Empowerment: As of 2023, over 8.6 lakh cooperative societies are active in the country, engaging around 29 crore members, with a substantial impact on economic empowerment.
2. Access to Credit: The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) reports that cooperative banks provide approximately 30% of the total rural credit in India.
3. Improved Agricultural Productivity: According to a study by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), agricultural cooperatives have contributed to a 20-25% increase in productivity among member farmers compared to non-members.
4. Market Access and Fair Pricing: The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) indicates that Indian agricultural cooperatives improve market access and pricing for their members, with price benefits estimated at 10-15% above local market rates.
5. Infrastructure Development: the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare reports over 50,000 cooperative societies have been involved in building irrigation facilities, storage units, and processing plants.
6. Employment Generation: The National Cooperative Union of India estimates that cooperatives create over 5 million jobs directly and indirectly across various sectors in rural areas
7. Social and Community Services: According to the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), cooperatives in India invest around ₹2,000 crore annually in community development projects, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure (source: NCDC Annual Report).
8. Skill Development and Capacity Building: The Ministry of Rural Development indicates that cooperatives provide training to over 2 lakh individuals annually, focusing on improving skills in agriculture, management, and technology
9. Mitigation of Rural Poverty: A study by the Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad (IIMA) suggests that cooperatives have helped reduce poverty in rural areas by increasing household incomes by up to 25% and providing economic stability
10. Strengthening Community Bonds: Research from the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA) highlights that cooperatives enhance community cohesion, with 60% of cooperative members reporting stronger social ties and a sense of collective responsibility

Critical Issues Impacting Cooperative Societies:
1. Internal Disputes: According to a survey by the National Cooperative Union of India (NCUI), about 30% of cooperatives face significant internal conflicts that adversely impact their operational efficiency and governance.
2. Lack of Management Expertise: Many cooperatives struggle with inadequate management expertise due to limited financial resources. This shortfall in skilled management can result in poor financial performance, mismanagement, and missed opportunities.
3. Government Interference: Large cooperatives often encounter bureaucratic hurdles and political interference, which can hinder their growth and operational efficiency.
4. Resource Limitations: Data from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) shows that approximately 35% of rural cooperatives face severe funding shortages, particularly in their initial stages.
5. Limited Market Access and Competition: According to the NABARD report 25% of Cooperatives in rural areas often face difficulties in accessing broader markets due to inadequate infrastructure and competition from larger businesses.
6. Technological Lag: Many cooperatives, especially in rural areas, lag in adopting modern technologies and digital tools. This technological gap leads to inefficiencies in operations and limits their market connectivity.
7. Inadequate Training and Capacity Building: The National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) found that around 50% of cooperatives lack access to comprehensive training programs, affecting their overall performance
8. Weak Governance Structures: Reports suggest that about 35% of cooperatives suffer from weak governance practices, impacting their transparency and effectiveness
9. Resistance to Change: Research by the ICAR highlights that resistance to change is a significant challenge for 30% of agricultural cooperatives, affecting their ability to innovate
10. Dependency on External Funding: Many cooperatives around 25% are heavily dependent on external funding from government grants, subsidies, or donor support. This dependency creates financial instability if such funding sources are reduced or discontinued.
Strategies for Enhancing Cooperatives in India
Improving Access to Capital: Strengthen the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF) to support cooperative enterprises in rural areas with essential infrastructure investments.
Developing Infrastructure: The government can take the lead in developing infrastructure such as The Karnataka State Cooperative Agricultural and Rural Development Bank (KSCARB) funds cold storage and transport facilities.
Leadership Training: Provides training through The Cooperative Development Foundation (CDF) to improve governance, strategic planning, and management skills for cooperative leaders.
Market Linkages: Adopt Amul’s model of connecting dairy farmers to broader markets for other sectors, leveraging its extensive network and marketing strategies.
Product Diversification: Apply successful dairy models to other sectors, as demonstrated by the Maharashtra State Cooperative Cotton Growers Marketing Federation (MSCCGMF) expanding into cotton processing and value-added products.
Leveraging Technology and Innovation: Enhance the Digital Green platform’s reach to provide agricultural cooperatives with digital tools for training and market information.
Inclusive Membership: The wider membership like the Kudumbashree program in Kerala which promotes women’s cooperatives, empowering women
Policy Support: Recent initiatives like Sahkar se Samridhi (Prosperity through Cooperatives) need consistent policy support for the healthy growth of cooperatives.
Social Projects: the cooperatives should take projects with high social impacts, such as the Rural Development Cooperative Society (RDCS) in Andhra Pradesh engages in community projects like building schools and health clinics to address local needs.
Performance Metrics: The Cooperative Auditors Association of India (CAA) provides tools and guidelines for evaluating cooperative performance, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Conclusion:
Cooperatives are crucial to the vitality of India’s rural economy and agricultural development. While recent government initiatives, such as hosting the first-ever conference of the International Cooperatives Alliance, are commendable, significant challenges remain. It is essential to take more prompt actions and support these initiatives to ensure that cooperatives become a key vehicle for a developed India by 2047.
PRELIMS QUESTION:
Q. With reference to the Cooperatives in India Consider the following statements:
1. To form cooperatives is the fundamental right under the constitution of India.
2. The States only regulate the multi-state cooperatives under entry 44 of the seventh schedule.
3. The cooperatives aim to boost the rural economy by providing membership to diverse sections.
4. Tamil Nadu has the highest number of cooperatives in India.
How many of the above-given statements are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. Only three
D. All four
ANSWER: B
MAINS QUESTION:
India has the highest number of cooperatives in the world. However, their potential to contribute to the rural economy has been constrained by various challenges. What are the ways to unlock and utilize this untapped potential?
(250 words 15 marks)





No Comments