24 Jul Walrasian Approach
Walrasian Approach to Price Determination – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Introduction
The Walrasian Approach, formulated by French economist Léon Walras in the late 19th century, is a foundational framework in microeconomic theory. Unlike Marshall’s partial equilibrium approach, Walras’s model attempts to explain price determination by examining the interdependence of all markets simultaneously—a concept known as general equilibrium. This approach is a cornerstone of modern economic theory and is essential for UPSC aspirants taking Economics as their optional subject.
1. Overview of Walrasian General Equilibrium
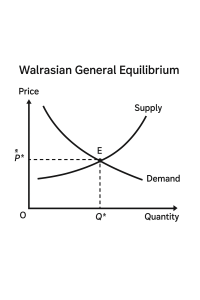
Walras’s theory is based on the idea that in an economy with multiple markets, equilibrium is achieved only when supply equals demand in all markets at the same time. It emphasizes:
- Simultaneous determination of prices in all goods and factor markets
- Dependence of each market on the conditions of all other markets
- Mathematical formulation using a system of simultaneous equations
Walrasian Equilibrium for UPSC CSE
2. Key Concepts in Walrasian Model
a. General Equilibrium
This refers to a situation where all markets in the economy are in equilibrium. It implies:
- Market clearing: Demand equals supply in each market
- Agents are maximizing utility or profits
- No unintended inventory accumulation or shortages
Best economics optional coaching for upsc
Best economics optional teacher for upsc
best economics optional test series
b. Tâtonnement Process (Groping or Auctioneer Mechanism)
Walras introduced the concept of a hypothetical auctioneer who adjusts prices based on excess demand or supply. The process is as follows:
- The auctioneer announces a set of prices.
- All buyers and sellers respond with their desired quantities.
- If there’s excess demand or supply, prices are revised.
- This process continues until equilibrium is reached in all markets simultaneously.
3. Mathematical Framework of Walrasian Approach
Walras’s model uses a system of equations where:
- Each equation represents the excess demand function for a good
- Equilibrium is achieved when all excess demand functions are zero
- The number of equations is equal to the number of markets
These equations are interlinked and must be solved simultaneously—a sharp contrast from the sequential approach of partial equilibrium analysis.
4. Assumptions of the Walrasian Model
- Perfect competition exists in all markets
- Consumers and producers are rational and maximize utility/profit
- No externalities or public goods
- Markets are complete and all goods are tradable
- Information is perfect and symmetric
5. Criticism of the Walrasian Model
- Highly abstract and unrealistic: Assumptions like perfect information and complete markets are rarely met.
- No time dimension: The model is static and ignores dynamic changes over time.
- No money or financial markets: The role of money is completely ignored in the basic Walrasian model.
- Tâtonnement is hypothetical: Prices do not adjust without transactions in real markets.
6. Relevance of Walrasian Approach Today
Despite criticisms, Walrasian theory remains a cornerstone of modern economics:
- Forms the basis of computable general equilibrium models (CGE) used in policy simulations
- Foundation for modern welfare economics
- Used to understand market efficiency, interdependence, and resource allocation
7. Infographic
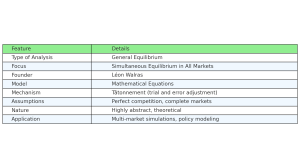
Walrasian Approach Infographic
8. Mind Map
GS paper 4 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 3 syllabus and study plan
9. Walras vs Marshall: A Quick Recap
- Marshall: Partial equilibrium, individual markets, graphical method
- Walras: General equilibrium, all markets, mathematical model
- Marshall’s method is practical for real-world application; Walras’s is theoretical and foundational
10. Previous Year UPSC Questions (Economics Optional)
- 2021: Distinguish between general and partial equilibrium analysis.
- 2018: Discuss the Walrasian process of price determination through the tâtonnement process.
- 2016: Explain the conditions for general equilibrium in a Walrasian framework.
11. Probable Questions for UPSC Prelims and Mains 2025
- Mains: Explain the Walrasian general equilibrium model and its relevance to modern economic policy.
- Mains: What are the key assumptions and criticisms of the Walrasian price determination approach?
- Prelims: The tâtonnement process in the Walrasian model refers to:
- Prelims: General equilibrium in the Walrasian sense is achieved when:
12. Conclusion
The Walrasian Approach offers a mathematically rigorous and theoretically elegant way of understanding price determination in an interconnected economy. While the assumptions may seem restrictive, the model remains relevant in academic and policy circles. For UPSC aspirants, mastering this approach is essential to tackle conceptual and applied questions in microeconomics.




No Comments