01 Aug White Label ATMs (WLAs)
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “White Label ATMs (WLAs)”. The topic “White Label ATMs (WLAs)” has relevance in the Economy section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About White Label ATMs (WLAs) ?
Types of ATM?
For Mains:
GS 3: Economy
Major Functionalities of an ATM?
Advantages of an ATM?
Limits of an ATM?
Why in the news?
White Label ATMs (WLAs) are expected to drive ATM spread across India with a greater focus on tier III to VI centres, said Union Minister of State for Finance, Bhagwat Kisanrao Karad
White Label ATMs (WLAs)
Definition and Ownership:
- ATMs set up, owned, and operated by non-banks are called White Label ATMs (WLAs).
- Non-bank ATM operators are authorized under the Payment & Settlement Systems Act, 2007 by the RBI.
- WLAs provide banking services to customers using debit/credit/prepaid cards issued by banks.
Steps to Enhance WLA Presence and Viability:
Cash Sourcing Flexibility:
- WLAs are allowed to source cash from retail outlets, Reserve Bank, currency chests, and any scheduled bank, including Cooperative Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- This addresses cash sourcing constraints faced by WLAs, especially after demonetization.
Expanded Services and Partnerships:
- White Label ATMs (WLAs) are allowed to provide bill payment and interoperable cash deposit services
- They can display advertisements for non-financial products/services, increasing revenue streams.
On-Tap Authorization:
- RBI introduced on-tap authorization for WLAs, simplifying the approval process to encourage more non-bank players to enter the ATM industry. This fosters greater competition and expansion of the WLA network.
Driving ATM Penetration:
- WLAs have a vital role in attaining this goal, as they provide convenient banking services to a wider range of customers. It focuses on expanding ATM penetration in Tier III to VI centers to improve banking accessibility in underserved areas. WLAs play a crucial role in achieving this objective, offering convenient banking services to a broader customer base.
Facilitating Consumer Complaints and Protection:
- The Consumer Education and Protection Department of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is responsible for handling complaints related to White Label ATMs (WLAs).
- Initiatives like the National Strategy for Financial Education (NSFE) 2020-2025 promote education and financial literacy.
Major Functionalities of an ATM:
- Cheque Deposition: Some ATMs allow customers to deposit cheques directly into their bank accounts, making it convenient for them to perform this banking task without visiting a branch.
- Cash Withdrawals: One of the primary functions of ATMs is to dispense cash to customers, allowing them to withdraw money at any time.
- Transferring Funds: Many ATMs enable fund transfers between the customer’s accounts linked to the ATM card.
- Verify Account Balance: Customers can check their account balances through the ATM, providing them with real-time information about their finances.
- Additional Services: ATMs often offer additional banking services like mobile recharges, bill payments, ticket booking, and more, providing convenience to users.
- Security: ATMs ensure secure transactions through encrypted channels, protecting customers’ financial data during transactions.
- Customer Authentication: Each transaction at an ATM requires customer authentication through individual PINs and card numbers, ensuring security.
Advantages of an ATM:
- Time-Saving: ATMs offer quick and efficient banking services, saving customers’ time by providing access to cash and various banking functionalities 24/7.
- 24/7 Availability: ATMs operate round the clock, allowing customers to access banking services even outside regular banking hours.
- Security: ATMs maintain high-security standards, protecting customer data and transactions with encryption and secure authentication measures.
- Authentic Accessibility: Customers can access their accounts securely using their unique PINs and card details, ensuring only authorized users perform transactions.
- Wide Network: ATMs are widely available, creating a vast network of banking services that customers can access conveniently.
Limits of an ATM:
- Technical Errors: ATMs may occasionally encounter technical issues, leading to service disruptions or transaction failures.
- Transaction Limits: There are limits on the amount of money that customers can withdraw or transfer in a single transaction or within a specific time frame.
- Limited Functionalities: While ATMs offer essential banking services, some complex transactions may require visiting a bank branch or using online banking platforms.
- Transaction Charges: Customers may incur transaction charges for certain types of ATM transactions, especially when using ATMs of other banks or exceeding transaction limits.
Q.1 Which of the following statements are true regarding White Label ATMs (WLAs) and their enhancement in India?
- WLAs are owned and operated by non-bank entities.
- WLAs are not allowed to offer bill payment and cash deposit services, limiting their revenue streams.
- WLAs primarily focus on expanding ATM penetration in metropolitan cities to improve banking accessibility.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a)
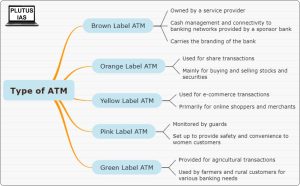
Q.2 Match the types of ATMs with their respective descriptions:
- Orange Label ATM
- Yellow Label ATM
- Pink Label ATM
- Green Label ATM
Descriptions:
(A) Used for share transactions; Mainly for buying and selling stocks and securities.
(B) Used for e-commerce transactions; Primarily for online shoppers and merchants.
(C) Set up to provide safety and convenience to women customers.
(D) Provided for agricultural transactions.
Options:
(a) 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
(b) 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-D
(c) 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
(d) 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
Answer: (c)
Q.3 Discuss the significance of ATMs in facilitating financial inclusion and the challenges faced in achieving widespread ATM penetration, particularly in rural and underserved areas.




No Comments