09 Aug Constitution and Constitutionalism
Constitution and Constitutionalism – UPSC Law Optional (Paper 1) Notes
Exam Focus: This comprehensive note covers the meaning, scope, evolution, and essential features of the Constitution and Constitutionalism from a UPSC Law Optional perspective. It also includes key case laws, challenges, comparative insights, previous year UPSC questions, probable Prelims and Mains questions, and visual aids like infographics and a high-resolution mind map.
1. Introduction
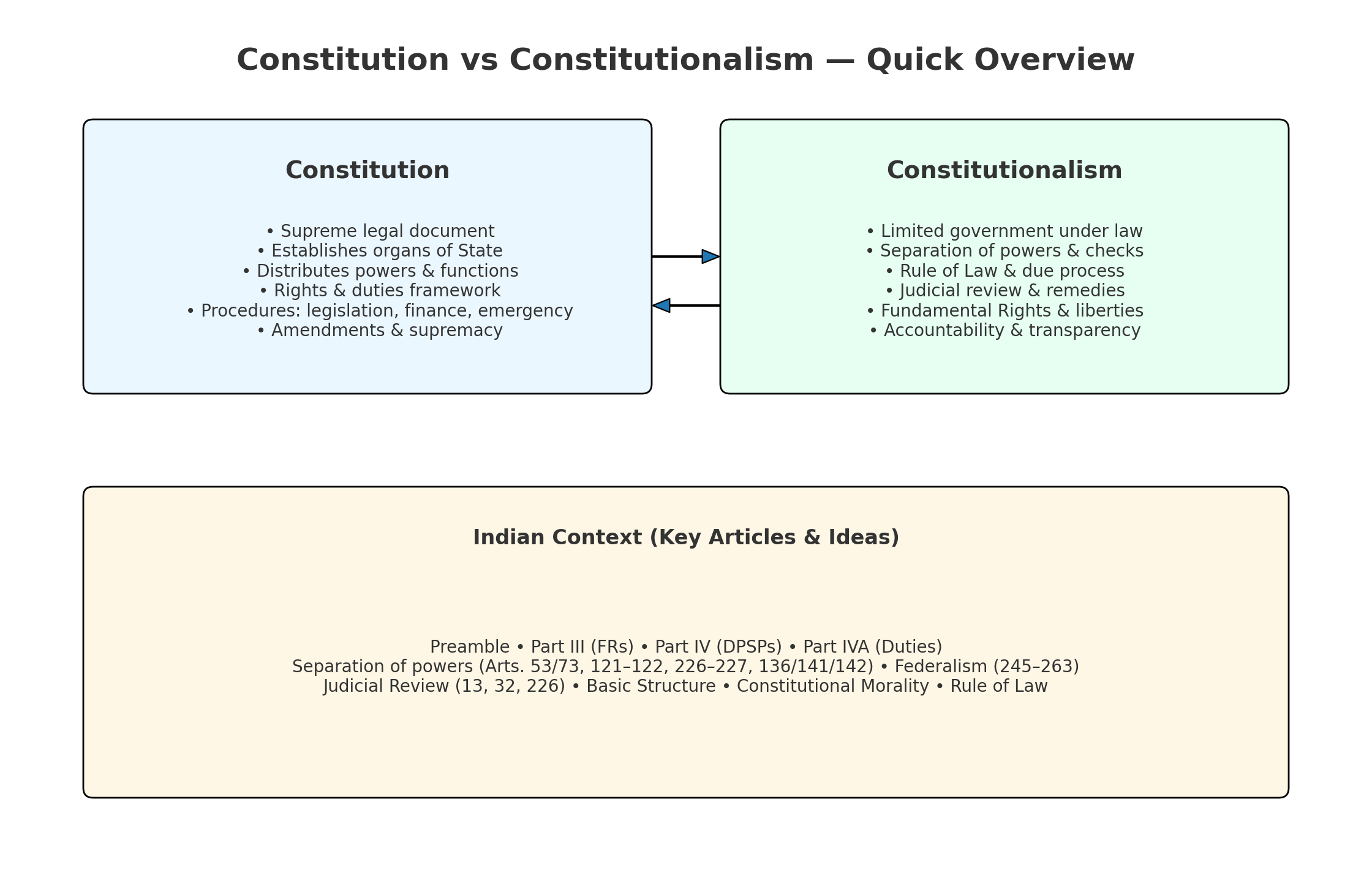
The terms Constitution and Constitutionalism are related but distinct. A Constitution is the fundamental legal document of a State that defines its political structure, allocates powers, and guarantees rights. Constitutionalism, however, is the philosophy that government powers must be limited and exercised in accordance with the Constitution, ensuring accountability, rights protection, and the rule of law.
2. Meaning of Constitution
A Constitution is the supreme law of a country. It lays down the framework for governance, the composition of different organs of the State, the distribution of powers between them, and the rights and duties of citizens. It can be written (India, USA) or unwritten (UK).
Best Law optional coaching for upsc
Best law optional teacher for upsc
Best coaching for law optional
3. Purpose and Features of a Constitution
- Establishes government organs and their powers
- Provides for separation of powers
- Protects fundamental rights
- Defines amendment procedures
- Ensures rule of law
4. Meaning of Constitutionalism
Constitutionalism is a governance philosophy emphasizing limited government under the Constitution. It is not enough to have a Constitution; there must be mechanisms to restrain arbitrary power. Constitutionalism safeguards liberty, enforces the rule of law, and upholds democratic accountability.

5. Evolution of Constitutionalism
The idea traces back to Magna Carta (1215) in England, American and French Revolutions, and Enlightenment philosophies. In India, constitutionalism developed during the colonial period through the Government of India Acts and matured post-independence under the 1950 Constitution.
6. Essential Features of Constitutionalism
- Rule of Law
- Separation of Powers
- Judicial Review
- Fundamental Rights
- Federalism
- Constitutional Morality
- Checks and balances

7. Constitution vs Constitutionalism
| Constitution | Constitutionalism |
|---|---|
| Written document defining government structure | Philosophy ensuring limited, accountable governance |
| Can exist in authoritarian regimes | Requires democratic principles and checks |
| Descriptive in nature | Normative and prescriptive |
8. Constitutionalism in India
In India, constitutionalism is embedded through the Preamble, Fundamental Rights (Part III), Directive Principles (Part IV), Fundamental Duties (Part IVA), separation of powers, judicial review, and the Basic Structure doctrine.
Best PSIR optional teacher for upsc
Best coaching for PSIR optional
Best PSIR optional coaching online
9. Limitations on Government Power
- Judicial review of legislative and executive actions
- Basic Structure doctrine preventing amendment of core constitutional features
- Independent institutions (ECI, CAG, UPSC)
- Parliamentary oversight
10. Rule of Law, Separation of Powers, Judicial Review
Rule of Law: All are equal before the law; no one is above it.
Separation of Powers: Distinct legislature, executive, judiciary.
Judicial Review: Power of courts to strike down unconstitutional acts.
11. Landmark Case Laws
- Keshavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala – Basic Structure doctrine
- Indira Nehru Gandhi v. Raj Narain – Rule of law as basic structure
- Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India – Due process and expanded Article 21
- IC Golaknath v. State of Punjab – Limitations on Parliament’s amending power
12. Challenges to Constitutionalism in India
- Misuse of ordinances and emergency provisions
- Weakening of institutional independence
- Over-centralization of power
- Delay in judicial processes
13. Comparative Perspective
UK: Unwritten constitution, conventions dominate.
USA: Rigid written constitution, strong judicial review.
India: Blend of rigid and flexible provisions, parliamentary sovereignty limited by Basic Structure.
14. Previous Year UPSC Law Optional Questions
- Discuss the concept of Constitutionalism. How is it different from having a Constitution?
- Examine the role of the Indian Judiciary in strengthening constitutionalism.
- Explain the Basic Structure doctrine and its significance for constitutionalism in India.
15. Probable Prelims Questions
- Which of the following is NOT a feature of constitutionalism? (a) Rule of Law (b) Unlimited Government (c) Separation of Powers (d) Judicial Review
- Which Article empowers the Supreme Court to enforce Fundamental Rights? (a) 32 (b) 226 (c) 131 (d) 136
16. Probable Mains Questions
- ‘A Constitution without constitutionalism is only a façade.’ Discuss with reference to India.
- Critically evaluate the challenges to constitutionalism in contemporary India.
- Compare the approach of India and the USA towards constitutionalism.
17. Conclusion
Constitutionalism transforms the Constitution from a legal document into a living framework for accountable governance. For UPSC Law Optional students, mastery over this topic means understanding both the text and the underlying philosophy, citing landmark cases, and applying them to contemporary issues.
Tags: UPSC Law Optional, Constitution, Constitutionalism, Rule of Law, Separation of Powers, Judicial Review, Basic Structure Doctrine, Fundamental Rights, Comparative Constitutional Law, Indian Polity
GS paper 4 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 3 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 2 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 1 syllabus and study plan




No Comments