25 Aug INDIA – AFRICA RELATIONS
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “INDIA – AFRICA RELATIONS”. The topic “INDIA – AFRICA RELATIONS” has relevance in the International Relations section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
Significance of Africa for India?
Significant Achievements in India-Africa Relations?
For Mains:
GS 2: International Relations
Challenges in India-Africa Relations?
Recommendations for Deepening India-Africa Ties?
Why in the news:
During its G20 presidency, India achieved a significant milestone by advocating for the inclusion of the African Union as a member, a historic stride emphasized by the Indian Prime Minister’s vocal stance.
Significance of Africa for India:
Economic Growth and Potential:
- Several of the world’s fastest-growing economies, including Rwanda, Senegal, and Tanzania, are located in Africa, positioning it as a prominent growth pole on the global stage.
- Over the past decade, Africa’s real GDP, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa, has more than doubled its growth rate from the 1980s and 90s.
- With a combined GDP of 2.5 trillion dollars, Africa offers an extensive and untapped market for goods and services.
Resource Abundance:
- Africa is projected to account for over half of the global population growth, estimated at 1.7 billion by 2050. This growth translates into a young and dynamic workforce, an expanding consumer base, and rising disposable incomes.
- Africa is rich in crucial resources that India lacks in sufficient quantities, including crude oil, natural gas, pulses, lentils, leather, gold, and other metals.
- Africa boasts 30% of the world’s mineral reserves, 12% of its oil, and 8% of its natural gas.
- Countries like Namibia and Niger stand among the top global uranium producers.
- South Africa holds the position of the world’s largest producer of platinum and chromium.
Strategic Partnerships:
- Strengthening ties with African nations enhances India’s geopolitical influence and promotes a balanced and diversified global engagement strategy.
- Africa’s proximity to major maritime routes can enhance India’s maritime security and trade connectivity.
- Collaboration with African nations in the energy sector, such as oil and natural gas, can contribute to India’s energy security and diversification of energy sources.
Significant Achievements in India-Africa Relations
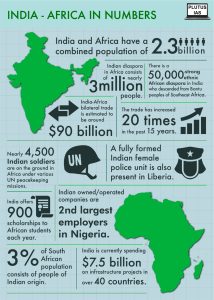
- Economic Cooperation: India’s engagement with Africa has led to significant economic cooperation. The continent provides an untapped market for Indian goods such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and light machinery. Over the years, India’s total goods trade with Africa has increased, with a notable rise from USD 68.54 billion to USD 90.52 billion between 2011 and 2022. India also achieved a positive trade balance with Africa in 2022.
- Development Assistance: India has played an active role in African development through initiatives like the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program. This program provides training and capacity-building opportunities for African professionals. Furthermore, India has extended lines of credit and grants for various development projects, including infrastructure, agriculture, and capacity building.
- Health Collaboration: Indian pharmaceutical companies have contributed to improved healthcare access in African nations by supplying affordable generic medicines. India’s support extends beyond medicines, as it has deployed medical teams and provided technical assistance to combat diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and Ebola. This collaboration has made a substantial impact on healthcare systems in the region.
- Defence Cooperation: The signing of Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) with all African nations on the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) underscores the growing defence engagement. The India-Africa Defence Dialogue (IADD) held at ministerial levels and trilateral maritime exercises, like the one with Tanzania and Mozambique, further enhanced regional maritime cooperation.
- Technology and Digital Cooperation: Under initiatives like the Pan African e-Network Project, India has set up a fiber-optic network to provide satellite connectivity, tele-medicine, and tele-education to African countries. The subsequent phases, e-VidyaBharti and e-ArogyaBharti (e-VBAB), introduced in 2019, focus on providing free tele-education to African students and continuing medical education for healthcare professionals. These efforts are advancing technological collaboration and capacity-building in the region.
Challenges in India-Africa Relations?
Addressing Internal Challenges:
- Countries like Ethiopia, Sudan, and the Central African Republic face internal turmoil, including insurgency, ethnic violence, and terrorism. India needs to navigate these complexities to foster stable partnerships.
Balancing External Competition:
- Various external players such as China, Russia, the United States, the European Union, Japan, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates are vying for influence in Africa.
- India must navigate this competitive landscape to ensure its engagements are mutually beneficial and aligned with African interests.
Counteracting China’s Dominance:
- China’s extensive involvement since 2000 poses a challenge for India in terms of economic partnerships, infrastructure development, and resource supply.
- India must offer compelling alternatives that resonate with African nations while acknowledging China’s contributions.
Infrastructure Deficit and Connectivity:
- Many African countries struggle with inadequate infrastructure, hindering seamless connectivity and trade. India’s engagement must include addressing these infrastructure gaps to enable sustained economic growth.
Cultural and Socio-Economic Differences:
- Cultural nuances and socio-economic disparities across African countries can impact the effectiveness of India-Africa collaborations. Tailoring strategies and initiatives to suit diverse contexts is essential.
Governance and Corruption Challenges:
- Governance issues and corruption prevalent in some African nations can hinder transparent and efficient project implementation. Building mechanisms for good governance and accountability is crucial.
Recommendations for Deepening India-Africa Ties
Strengthening Political and Diplomatic Cooperation:
- Revive periodic leaders’ summits, such as the India-Africa Forum Summit.
- Sustain the Indo Africa Forum Summit, a Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) initiative promoting cooperation in human resource development and agriculture.
Enhancing Defence and Security Cooperation:
- Deploy more defence attachés in African nations to intensify defence-related dialogue.
- Strengthen maritime cooperation and offer Lines of Credit for defence exports.
- Foster collaboration in counterterrorism, cybersecurity, and emerging technologies.
Deepening Economic and Development Cooperation:
- Establish an Africa Growth Fund (AGF) to enhance finance access for India-Africa trade.
- Implement measures to bolster project exports and shipping cooperation.
- Emphasize trilateral cooperation and expand joint ventures in science and technology.
Increasing Socio-Cultural Cooperation:
- Facilitate greater engagement between Indian and African universities, think tanks, civil society, and media.
- Create a dedicated National Centre for African Studies.
- Name Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) and Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) scholarships after notable African figures.
- Simplify visa procedures for African students pursuing higher education in India and provide short-term work visas.
By adhering to these recommendations, India can solidify its alliance with Africa, tapping into the continent’s potential while elevating its global standing. This comprehensive approach would not only benefit India and Africa but also contribute to international cooperation and development.
plutus ias current affairs eng med 25th August 2023
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- Africa’s real GDP growth has decreased over the past decade.
- India advocated for the exclusion of the African Union from the G20.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER: D
Q.2 What are the objectives of the Pan African e-Network Project initiated by India?
- To provide satellite connectivity to African countries.
- To provide telemedicine services to African countries
- To provide tele-education to African countries
How many of the above statement/s is/are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ANSWER: C
Q.3 “India-Africa relations have witnessed significant advancements over the years .However, challenges and opportunities persist in this dynamic partnership.” In light of this statement, discuss the key achievements, challenges, and future prospects of India-Africa relations.




No Comments