05 Jul India’s presence in the Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission
(This article is related to the section ‘ Indian Constitution and Governance, International Relations and Important International Institutions, Important Authorities and Commissions’ of UPSC Civil Services Mains General Studies Paper-2 and ‘ Development of Indian Economy, Important Facts about Indian Agriculture and Food Processing’ of Mains General Studies Paper-3 and ‘ Codex Alimentarius Commission, Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, State Food Safety Index, Food Safety Mitra, Eat Right Station ’ of UPSC Prelims. It also includes suggestions from the PLUTUS IAS Team. This article is related to ‘ India’s presence in the Executive Committee of Codex Alimentarius Commission’ of ‘ Daily Current Affairs ’.)
Why in the News ?

- India recently participated in the 86th session of the Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC).
- In this session, India has made significant contributions in promoting the quality standards of spices such as black cardamom, vanilla and turmeric.
- As an important producer and exporter of these spices, India’s participation is important in facilitating international trade.
- India has supported the advancement of standards for designated vegetable oils, including guidelines to control Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, and standards for the safe use and reuse of water in food production and processing. Have agreed.
Codex Alimentarius Commission ( CAC ) :
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) is an international food standards body.
- The main objective of this body is to protect the health of consumers and ensure fair practices in the food trade.
- This international organization was jointly established in May 1963 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).।
- Under this, various food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice are prepared.
- The standards and codes set forth herein generally apply to sanitary practices, labeling, contaminants, additives, inspection, certification, nutrition, and handling of residues of veterinary drugs and pesticides.
- Currently the CAC has a total of 189 members, including 188 countries and the European Union.
- India became a member of CAC in 1964.
- Commodity standards under the Codex refer to specific products, while regional standards apply to related regions.
86th Session of the CAC Executive Committee (CCEXEC) :
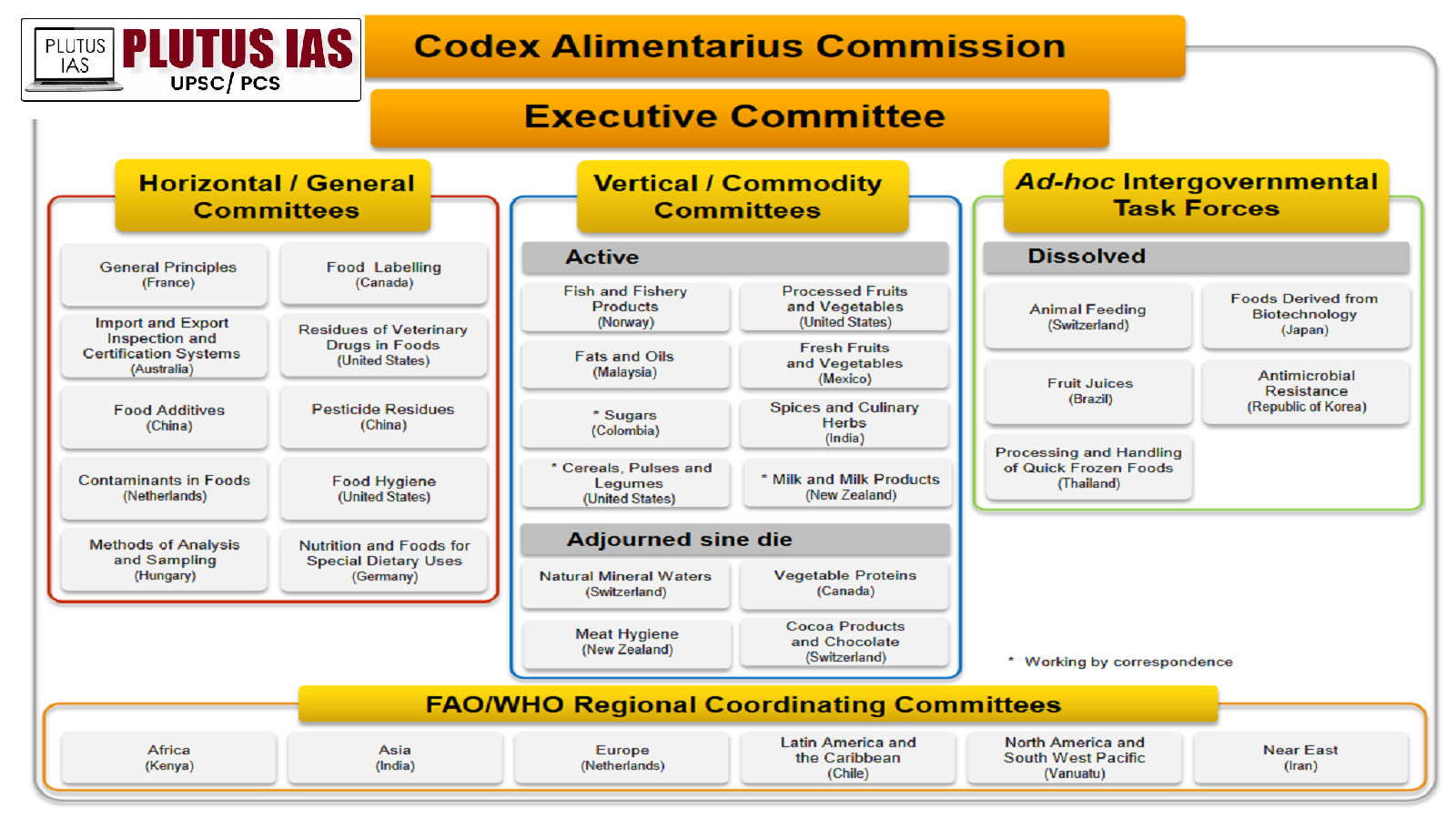
- Under the leadership of the CEO of Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), India actively participated in the 86th session of the Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CCEXEC) held at the FAO Headquarters in Rome.
- The principal function of CCEXEC is to review new work proposals and monitor the progress of standards development.
- During the 86th session of the Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CCEXEC), India strongly supported the development of beads of various spices including black cardamom, turmeric and vanilla.
- This initiative holds special significance for India, as India is a major producer and exporter of these spices. Therefore, this will make it easier for India to do international trade.
- Additionally, India supported the advancement of standards for vegetable oils, guidelines for the control of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli, and safe use and reuse of water in food production and processing. Did.
- India also supported the proposal to develop a guidance by Codex on food safety considerations related to the use of recycled materials in food packaging.
- This initiative is extremely important in addressing global challenges like climate change, environmental protection and sustainability.
- Finally, India shared its experiences with guidelines developed by FSSAI on recycling of post consumer PET (polyethylene terephthalate) for food contact applications.
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) :

- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is an autonomous statutory body.
- In India it has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- This body works under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare of India.
- It is a body responsible for protecting and promoting public health by regulating and supervising food safety and quality in India.
- FSSAI is headquartered in New Delhi and has six regional offices located in Delhi, Guwahati, Mumbai, Kolkata, Cochin and Chennai.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India enforces various provisions of the Food Safety Acts of the states.
- FSSAI works to ensure safe production, storage, distribution, sale and import of nutritious food for human consumption.
- Apart from this, it helps in maintaining the prescribed standards of production and sale of food items at all the states, district and gram panchayat levels of the country.
- It also checks the quality of retail and wholesale food items from time to time.
- Its main objective is to formulate standards based on scientific facts for food items and to ensure the achievement of safe and complete diets for human consumption through controlling the production, storage, distribution, sale and import of food items.
Important initiatives related to food safety launched by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India :
State Food Security Index :
- FSSAI has developed the State Food Security Index (SFSI) to measure the performance of states on five parameters of food security.
Eat Right Awards :
- FSSAI has instituted the ‘Eat Right Awards’ to empower Indian citizens to make safe and healthy food choices and to recognize the contribution of food grain companies and individuals towards better health and well-being of citizens.
Eat Right Fair :
- Organized by FSSAI, this fair is an outreach activity to motivate citizens to eat right.
Eat Right India :
- The main objective of this initiative launched by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is to improve the quality and nutritional level of food in India. Under this, various aspects like healthy eating habits, safe food and sustainable food systems are emphasized.
Eat Right Station :
- This initiative launched by FSSAI aims to provide safe and nutritious food at railway stations. Under this, food vendors at railway stations are trained and certified as per the standards of FSSAI. Under this initiative it is ensured that passengers get clean and safe food.
RUCO (Reused Cooking Oil) :
- RUCO (Reused Cooking Oil) is an initiative that aims to reuse used cooking oil and convert it into biodiesel. Under this initiative, used oil is stored and used to make biodiesel. This can reduce environmental damage and promote a sustainable source of energy.
Food Safety Mitra :
- Under this program launched by FSSAI, trained professionals are appointed to ensure compliance of food safety standards in various food businesses. These friends help food businesses operate properly and help consumers get safe and healthy food.
100 Foods :
-
- The main objective of the 100 Foods program launched by FSSAI in India is to showcase the diversity and nutritional value of Indian food. It includes 100 major Indian food items, which are rich in various nutritional properties. The aim of this initiative is to make people aware about healthy and balanced diet.
- All these initiatives aim to improve the Indian food system as a whole and ensure availability of healthy and safe food.
Source – PIB and Economic Times.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 05th July 2024
Practice Questions for Preliminary Exam :
Q.1. With whom does the WTO cooperate to settle disputes related to the use of international food safety standards? ( UPSC – 2018 )
A. International Organization for Food Safety Standardization.
B. International Federation of Standards Users.
C. Food Safety and Standards Authority of India.
D. Codex Alimentarius Commission.
Answer – D
Practice Questions for Main Exam :
Q.1. What are the main challenges of the food processing sector in India and explain in detail and logically the main policies adopted by the Government of India to address the main challenges of the food processing sector. (UPSC CSE – 2019 Word Limit – 250 Marks – 15 )




No Comments