15 Dec National Energy Conservation Day
National Energy Conservation Day
The topic is based on the significance of National Energy Conservation Day. The article also tells how Energy conservation impacts Environment and climate change.
Relevance for Prelims: Energy conservation in India
Relevance for Mains: Steps taken by India to conserve energy
Context: National Energy Conservation is celebrated every year on 14th December.
Reason for the celebration of National Energy Conservation Day
- It was Ministry of Power, Government of India launched the National Energy Conservation Awards in 1991 to recognize the contribution of industries and establishments in reducing energy consumption while maintaining production.
- National Energy Conservation Day is celebrated by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency.
- It was 1991 when the first awards were given.
- The major objective of declaring the day on making people aware of global warming and climate change.
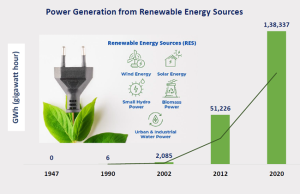
Renewable Energy Sources
The scenario of India’s power sector:
- India is considered as third largest consumer and producer of electricity worldwide, with an installed power capacity of more than 400 GW (as of October 2022).
- India stands in the top 5 positions in many renewable sector verticals. For example, Wind energy installation capacity in India (4th rank) and (5th rank) in terms of solar energy installation.
- The government announced in COP26 that the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy is working towards 500GW of installed electricity capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030.
Steps were taken by India for energy conservation:
- PAT Scheme: Perform Achieve and Trade Scheme is a market base mechanism to enhance the cost-effectiveness in improving energy efficiency in energy-intensive industries.
- Energy Conservation Building Code: It was developed in 2007 for commercial buildings to ensure energy efficiency.
India has progressively decoupled economic growth from greenhouse gas emissions. For example, the Net Zero Emissions target by 2030 by Indian Railways alone will reduce emissions by 60 million tonnes annually. Similarly, India’s massive UJALA LED bulb campaign is reducing emissions by 40 million tonnes annually. To further complement these ongoing efforts, India launched the National Hydrogen Mission in 2013 to make India the world’s largest hydrogen hub.
Even though it supports the second-largest population in the world, India’s sustained efforts have ensured that its per capita CO2 emissions are much lower than the global average. The US emits 14.7 tonnes per capita, China emits 7.6 tonnes per capita, and India’s CO2 emissions amount to 1.8 tonnes per capita.
The global power sector is undergoing an accelerated transformation due to technological innovations and response to climate change protocols. At COP-21 in Paris in 2015, India committed to a 40% share of power generation from non-fossil fuel sources. We have achieved this target a decade ahead of the 2030 timeline.
India has always shown its willingness in leadership to fight climate change. The country’s vision is to achieve Net Zero Emissions by 2070, in addition to attaining the short-term targets which include:
- Increasing renewables capacity to 500 GW by 2030,
- Meeting 50% of energy requirements from renewables,
- Reducing cumulative emissions by one billion tonnes by 2030, and
- Reducing emissions intensity of India’s gross domestic product (GDP) by 45% by 2030.
India’s experience will be valuable to other developing nations as they translate their climate pledges into actions and undertake energy transitions toward a more sustainable energy future.
Previous Year Questions:
Q1- On which of the following can you find the Bureau of Energy Efficiency Star Label? (2016)
- Ceiling fans
- Electric geysers
- Tubular fluorescent lamps
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
UPSC Previous Year Questions Mains
Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India at this conference?
Source:
IAS Current Affairs
For becoming an IAS officer, every aspirant have to clear the IAS examination process like Prelims, Mains, and Interview exam. If any UPSC aspirant wants to pass the UPSC examination, he/she has to enhance their general knowledge. Reading current affairs collaborates the examinee with increasing general knowledge. So read updated current affairs for your IAS exam preparation.
For reading the best and latest daily current affairs for the UPSC examination, please visit PlutusIAS current affair site and get Daily, Weekly, and Monthly current affairs.



No Comments