06 Jan National hydrogen mission
National Hydrogen Mission
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs for UPSC” and the topic is ‘The national hydrogen mission’ which is in news, it covers the “Infrastructure and energy sector of India” In GS-3, and the following content has relevance for UPSC.
For prelims: Facts about green hydrogen and different types of hydrogen.
For mains: GS-3, infrastructures from the Indian economy, about the green hydrogen mission
Why in news:
- India’s Rs 20,000 crore National Green Hydrogen Mission has been authorized by the Union Cabinet, which is presided over by the Prime Minister (NGHM).
- The National Hydrogen Mission (NHM), which the finance minister outlined in the Union Budget for 2021–2022, includes NGHM.
- On the occasion of India’s 75th Independence Day, the Indian Prime Minister also unveiled the National Hydrogen Mission.
Aim and objective of National Hydrogen Mission
- Making India a major hub for the production and export of green hydrogen is one of the goals.
- In order to satisfy India’s Nationally Determined Contributions, we must harness green hydrogen energy (NDCs).

Hydrogen
About green hydrogen
- A crucial industrial fuel, hydrogen is used to create steel, electricity, and ammonia, a crucial fertilizer, among other things.
- Green hydrogen is created when water is electrolyzed to separate into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity produced using renewable energy sources like solar or wind. This method of creating hydrogen is the most eco-friendly.
Extraction:
- The element hydrogen coexists with other elements.
- This means that in order to use it as a source of energy, it must be extracted from naturally existing substances like water (which is a combination of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom).
- Different colors represent different categories of hydrogen’s sources and production methods.
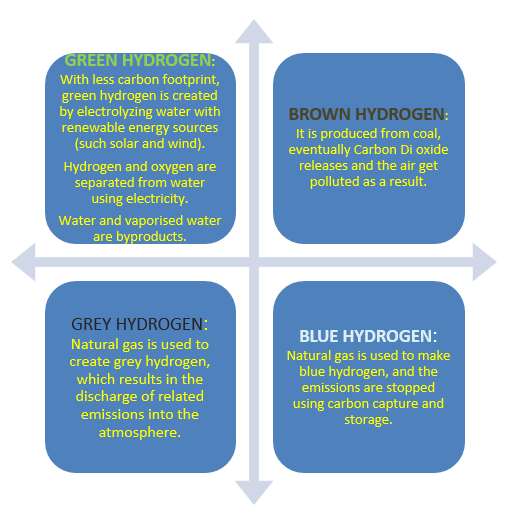
TYPES OF HYDROGEN
Other Colours of Hydrogen

Black hydrogen
- Bituminous coal is used to make Black hydrogen

Red hydrogen
- Biomass is used to make Red hydrogen

Pink hydrogen
- Nuclear power is used to make Pink hydrogen.

Yellow hydrogen
- Solar power or a mix of energy sources from the electrical grid is used to make Yellow hydrogen.
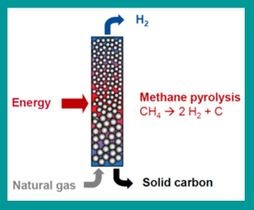
Turquoise hydrogen
- Methane pyrolysis is used to make Turquoise hydrogen
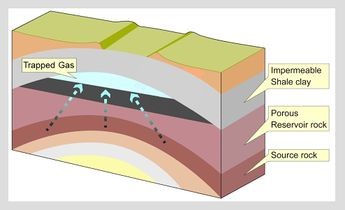
White hydrogen
- Naturally occurring geological hydrogen is called White hydrogen.
Key Elements
- The scheme implementation guidelines for the individual components will be developed by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- Production, use, and export of green hydrogen will all be facilitated by the NGHM.
- Pilot initiatives in developing end-use industries and supply chains will also be supported by the Mission.
- The creation of the Green Hydrogen ecosystem will be aided by the creation of an enabling policy framework.
- The Mission will enable the development of a framework for public-private partnerships in R&D. To create technologies that are competitive on a worldwide scale, R&D initiatives will be goal-oriented, time-bound, and appropriately scaled up.
How would the national hydrogen mission aid in the generation of green hydrogen
- According to the Ministry for New and Renewable Energy, the Mission would “enable demand generation, production, utilization, and export of Green Hydrogen.”
The program is divided into two umbrella sub-missions.
- Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition Programme (SIGHT), which will provide funding for household electrolyzer production and green hydrogen.
- Green hydrogen hub: The second is supported by pilot projects in newly emerging end-use markets and distribution networks. We will identify and create “Green Hydrogen Hubs” in states and regions that can support large-scale hydrogen production and/or use.
Concerns associated
- India will face competition from the roughly 500 hydrogen stations that are currently operational worldwide, most of which are in Europe, followed by Japan and South Korea. This is due to a lack of fuel station infrastructure.
- The method of producing hydrogen is energy-intensive and is still in its infancy. A lot of energy is needed to split methane or water. In addition, the current cost of the process is high.
- High R&D investment is needed for the newer technology to make the process affordable, workable, and scalable.
- the number of regulatory agencies: Red tape in government operations is brought on by the involvement of numerous Ministries and Departments.
- Risks related to the transportation of hydrogen: Because hydrogen is very combustible and challenging to move around, safety is the first priority.
Advantages:
- Positive aspects of green hydrogen.
- The development of green hydrogen export opportunities.
- Decarbonization of the transportation, industrial, and energy sectors
- Being independent decreases reliance on imported feedstock and fossil fuels.
- For India, made in India: building up domestic manufacturing capacity
- The creation of job opportunities.
- Creation of innovative technologies.
Significance:
- RE Capacity Enhancement: Establish a green hydrogen generation capability of at least 5 MMT (million metric tonnes) annually.
- a country-wide increase in associated renewable energy capacity of roughly 125 GW
- Boost up the investment
- More employment generation.
- Imports of fossil fuels have been reduced overall.
- Almost 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions must be reduced in order for the government to fulfill its COP 26 obligations.
- The best zero-emission solutions are those like this one. With only water-related tailpipe emissions, it is fully eco-friendly.
- Reduce emissions: emission into the atmosphere of gas or radiation, for example.
- Limited operation Because of how quiet the fuel cells are, they can be employed in tough environments like hospital buildings.
Way ahead:
- Alternatives that Reduce Emissions: Another option that several hydrogen councils are advocating for is “blue” hydrogen, which is grey hydrogen combined with additional installations for carbon capture and storage built within the manufacturing facility.
- National Hydrogen Mission (NHM) will see to it that the world’s and India’s clean energy supply chains are integrated.
- The success of NHM depends on interministerial and departmental coordination.
- NHM will make India a global leader in clean hydrogen energy and will ensure that the country’s aim of being carbon neutral is achieved.
Source:
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Daily Current affairs are the medium of attaining important news of the national and international world. There are several sources of reading current affairs in the market. Here, Plutus IAS is the best source of daily current affairs for the UPSC examination. So, From today collect the best daily current Affairs from us and read them properly for UPSC exam preparation.
Also, Get the latest Weekly, and Monthly Current Affairs for IAS exam preparation.




No Comments