06 Feb Renewable Energy in India
Renewable energy in India
This article covers “Daily current affairs for UPSC “and the topic is about ‘Renewable energy in India which is in news, it covers the “Indian Economy” In GS-3, and the following content has relevance for UPSC.
For Prelims: About renewable energy sources
For Mains: GS-3, infrrenewable energy in indiaastructure,Indian Economy
Context
- The world’s installed wind energy capacity is the fourth largest in India. The potential is larger and can be hastened, though, if the policies and bidding system are adjusted.
- According to the Union Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, the nation’s total installed capacity was 41.67 GW as of September 30, 2022. In the years 2020–21, almost 60.15 billion units were
- By 2022, the Indian government wants to have 175 GW of capacity for renewable energy. Achieving 60 GW of onshore and 5 GW of offshore wind energy capacity was a goal.
Renewable energy
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are regenerated more quickly than they are used up. Examples of such sources that are continually replenished are the sun and the wind. There are many different types of renewable energy all around us.
Renewable energy sources are frequently included when using the term “alternative energy.” It refers to alternate energy sources to the most popular non-sustainable sources, such as coal.
The most popular renewable energy sources currently are:
- Solar energy
- Wind energy
- Hydro energy
- Tidal energy
- Geothermal energy
- Biomass energy
Renewable Energy
Solar energy
- Solar energy is the most plentiful energy source available and may be used in cloudy conditions. The Earth absorbs solar energy at a pace that is around 10,000 times greater than the rate at which people use
- The quantity of solar energy that reaches the surface of the globe in a single hour exceeds the planet’s whole annual energy
- Solar technologies are capable of providing heat, cooling, natural lighting, power, and fuels for a variety of uses. Through photovoltaic panels or mirrors that concentrate solar radiation, solar technologies transform sunlight into electrical energy.
- India has a lot of solar energy potential. The energy incidence over India’s land area is around 5,000 trillion kWh every year, with the majority of areas receiving 4–7 kWh per sq. m. per day. In India, solar photovoltaic power may be efficiently harnessed and has enormous.
- India increased its grid-connected solar capacity by a total of 8 GW in the first eight months of 2022.
- Solar energy generation reached 73.48 Billion units for the financial year 2021-22.
- An increase of 22% over the previous year. The top three states for solar energy production were Rajasthan, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
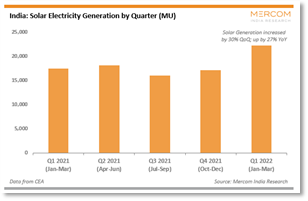
Solar Energy
Wind Energy
- Wind energy is the process of harnessing the kinetic energy of moving air by means of massive wind turbines that are installed on land (onshore), in salt water, or in freshwater (offshore). Despite the fact that wind energy has been used for thousands of years, onshore and offshore wind energy technology has lately progressed to maximize the quantity of electricity produced, with higher turbines and larger rotor diameters.
- Although average wind speeds vary widely by location, the globe’s technical potential for wind energy exceeds that of electricity production, and most locations of the world have the potential to support considerable wind energy
- According to Renewables 2022 Global Status Report, India ranked third globally for the total installed capacity of wind power (40.1 GW), behind China, the US and
- In the second quarter (Q2) of 2022, India installed 430.45 MW of wind power capacity, a 57% quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) increase compared to the 275 MW installed in the first quarter.
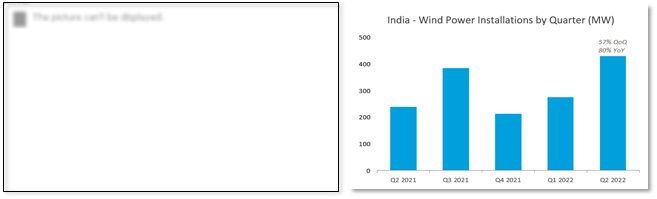
Wind Power Installation by Quarter
of 2022. According to the latest data given by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, the total number of wind installations in the nation is 40.8 GW.
- Top of the list was Gujarat, which added about 210.2 MW of wind capacity. With 72.3% of the total capacity, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Maharashtra remained the top markets for wind.
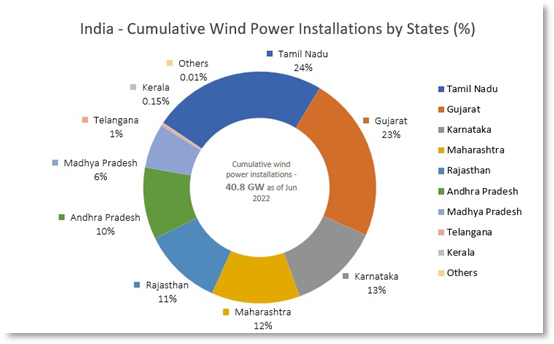
Wind Power Installation
Hydro-power Energy
- The largest renewable energy source in the electricity sector at the moment is hydro-power. It is dependent on typically consistent rainfall patterns. The energy of water flowing from higher elevations to lower elevations is captured by hydro-power.
- It can be produced by rivers and reservoirs. Run-of-river hydro-power facilities rely on the river’s available flow, whereas reservoir hydro-power plants use water that has been stored in a
- In addition to supplying energy, hydro-power reservoirs frequently serve as sources of drinking water, irrigation water, flood and drought control, navigation services, and energy.
- According to Renewables 2022 Global Status Report, India added 843 MW of hydro-power capacity in 2021, raising the total capacity to 3 GW.
- The top five hydroelectric power plants in the nation are located in the states of Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Maharashtra.
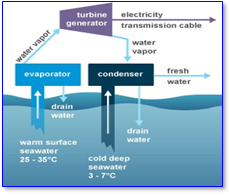
Ocean Energy/ Tidal energy
- Tides are used to power turbines twice daily in tidal energy, another sort of hydropower. While tidal flow isn’t constant, unlike some other hydro energy sources, it is incredibly predictable and may therefore make up for times when the tide current is weak.
- Tidal energy is now at the research and development (R&D) stage in India, according to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy. Low to moderate tidal wave power is predicted for the Gulf of Khambat, Gulf of Kutch, southern Gujarat, Palk Bay and Mannar Channel in Tamil Nadu, Hooghly River, South Haldia, and the Sunderbans in West Bengal.
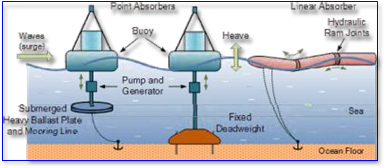
Ocean Energy
Geothermal energy
- Geothermal energy uses the thermal energy that exists within the Earth’s interior. Warming geothermal reservoirs can be accomplished using wells and other methods.
- Enhanced geothermal systems are ones that are naturally adequately hot but improved by hydraulic stimulation, whereas hydrothermal reservoirs are those that are naturally sufficiently hot and permeable.
Geothermal energy
- Once they reach the surface, fluids of various temperatures can be used to generate electricity. The technique for generating energy from hydrothermal reservoirs is established, dependable, and mature since it has been in use for more than a century.
- Rajgir in Bihar, Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh, Surajkund in Jharkhand, Tapoban in Uttarakhand, and the Sohana region in Haryana are among the interesting geothermal sites for direct heat usage applications. reservoir. The pressure of the deep reservoir is released as the water is pumped into the generator.
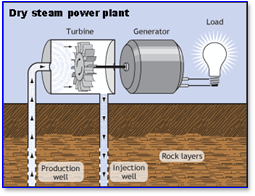
Geothermal Energy
Biomass energy
- Bioenergy is made from various organic resources, known as biomass, including wood, charcoal, dung, and other manures for the production of heat and power, as well as agricultural crops for the creation of liquid biofuels. The majority of biomass is used for cooking, lighting, and space heating by the poorest people in developing countries rural areas.
- Modern biomass systems make use of specialized plants or trees, waste materials from forestry and agriculture, and a variety of organic waste streams.
- Although at a lower rate than when fossil fuels like coal, oil, or gas are burned, burning biomass produces greenhouse gas emissions. However, given the potentially negative environmental effects linked to considerable increases in plantations for bioenergy and forests, as well as the consequent deforestation and land-use change, bioenergy should only be used in limited applications.
- The primary goal of the biomass power and co-generation program is to promote technologies that make the best use of the nation’s biomass resources for grid power Bagasse, rice husks, straws, cotton stalks, coconut shells, soy husks, de-oiled cakes, coffee trash, jute waste, groundnut shells, sawdust, and other biomass products are used to generate electricity.
- In the nation, more than 800 biomass power and bagasse/non-bagasse cogeneration facilities of 10170 MW capacity have been erected to supply electricity to the grid. Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh are the states that have taken the lead in putting bagasse cogeneration plants into The major States for biomass power projects are Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu.

Biomass energy
Current scenario of Renewable Energy in India
- Global Status Report (GSR 2022) presents a world map of country shares of renewable energy for the first time and emphasizes development in some of the top nations.
- A record 135 nations made the commitment to attain net zero greenhouse gas emissions by the year 2050 in the run-up to the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) in November 2021.
- However, only 84 of these nations had targets for renewable energy across the whole economy, and only 36 had targets for 100% renewable energy.
- REN21 (Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century)published the Renewables 2022 Global Status Report (GSR 2022). India was in third place behind China and Russia in terms of renewable energy installations in 2021.

Current scenario of Renewable Energy
Benefits of renewable energy
- Because weather disruptions in one region cannot be the same in other locations, solar and wind power plants might produce electricity with little or no interruption. however, it will provide electricity under typical circumstances in locations without electricity or in distant
- Zero Carbon Emissions: During renewable energy production, no greenhouse gases or other pollutants are
- Energy security: There is no chance that renewable resources will run out because they do not deplete over time. While fossil fuels (coal, gas, and oil) are thought to be finite resources, there is a good chance that they will eventually run
- Low maintenance costs: One benefit of solar energy is that there is almost no need to purchase fuel, and there is also less wear and tear because there is no movement of
- Reduce pollution: Renewable energy technologies have a positive impact on both air quality and human health.
- In order to accomplish Sustainable Development Goals, electricity is provided to the underprivileged via renewable energy. For example, installing solar panels allows the underprivileged to obtain
Challenges of Renewable Energy
- The majority of renewable energy facilities take up a lot of room. This raises the cost of the large land area as well as other difficulties regarding the purchase of
- Renewable energy sources are influenced by the weather, including solar, wind, and tide, and It becomes ineffective and impractical without the right weather conditions.
- To take advantage of economies of scale, it is necessary to put up huge projects for renewable This necessitates a sizable upfront investment, which may be a turnoff at first.
- Renewable energy sources require some kind of energy storage since their intermittent nature makes it difficult for them to consistently and carefully discharge electricity. Technologies for storing data are still quite expensive, despite the costs
Government Initiatives for generating Renewable Energy
- India was the first nation in the world to establish a ministry of non-conventional energy resources, which is today known as the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), which was founded in 1992. The Solar Energy Corporation of India, one of its public sector enterprises, is in charge of developing the solar energy sector in India.
- According to the Central Electricity Authority’s strategy framework, the nation wants to generate 57% of its total electricity from renewable sources by 2027. India plans to have 275 GW of renewable energy, 72 GW of hydroelectricity, 15 GW of nuclear energy, and roughly 100 GW from other zero-emission sources by 2027, according to its 2027
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is a group of 121 nations that was founded by India. The majority of these nations are sun-drenched countries that are entirely or partially located between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. In order to lessen reliance on fossil fuels, the alliance’s main goal is to promote efficient solar energy
- Biomass-based fuels are more calorie-dense and cleaner than conventional biomass. The government is also aiming for bio-CNG cars with a 20% petrol blend. Biomass energy production is preferable since it will clean up urban areas and lessen our reliance on foreign energy
- PM KUSUM: Farmers in the nation are encouraged to build solar pumps, grid-connected solar power plants, and other renewable energy sources. By 2022, the plan seeks to install 25,750 MW of solar and other renewable energy capacities.
- SRISTI is a program for sustainable rooftop implementation for solar transformation in India. The country’s beneficiaries will receive a financial incentive from the central government in exchange for establishing solar power plant rooftop
Way Ahead
- In order to facilitate the expansion of renewable energy, both intrastate and interstate transmission infrastructure should be
- To strengthen the institutional framework and enable the efficient flow of government funding. Strengthening the institutional framework is crucial in order to keep an eye on how government policies and initiatives are being carried out.
- It is essential to provide policy direction well in advance so that the private sector can make the appropriate plans because renewable energy requires significant investment to attain economies of
- It is crucial to identify the sectors with the highest energy consumption and link them with production sources to meet the fluctuating demand and maximize energy use. For instance, it is necessary to encourage the agricultural industry to use electricity at off-peak times
- The private sector does not enjoy frequent surprises or changes in policy. To instill confidence in the businesses, the government should define the geographical regions, integrate the grid, and concentrate on execution at the local level.
- We should concentrate on electric and hydrogen fuel cell-powered automobiles as these are the best ways to transition to renewable energy sources.
Conclusion
Renewable energy is without a shadow of a doubt the energy of the future. The current trajectory suggests that fossil fuel-based energy may be eliminated as early as 2050. This will result in a cleaner, greener planet and improve the quality of life on earth. To attain optimum efficiency, we must have a defined set of policy guidelines that examine the best combination of energy sources that are integrated into the grid.
Source:
Download the PDF now:
PLUTUS IAS CURRENT AFFAIRS 6th FEB 2023
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
The topic described above is related to Indian Economy. The article talks about the details of Renewable energy in India that are included under the topic of Daily Current Affairs for UPSC. Get the best daily current affairs for the UPSC examination free of cost. Also, Read the weekly, and monthly current affairs for IAS exam preparation.



No Comments