16 Jan India China trade deficit
India-China trade deficit
This article covers “Daily current affairs for UPSC” and the topic is about the ‘India China trade deficit ’ which is in the news, it covers “International relations” In GS-2 and GS-3, and the following content has relevance for UPSC.
For Prelims: India china trade ties, major import and export items
For Mains: GS-2, GS-3, India and its neighborhood, Growth, and development
How do the trade ties between China and India stand
- China is India’s second-largest trading partner after the US. One of the Biggest Partners.
- About 20 years ago, China’s ranking among trading partners was 10, but since 2002 or 2003, it has moved up the list.
- In 2011–12, 2013–14, 2017–18, and 2020–21, China was India’s largest trading partner.
- For the years 2021–22, the US and China were India’s top two commercial partners, followed by the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Singapore, Hong Kong, Indonesia, South Korea, and Australia.
| India’s imports from China |
|
| India’s exports to China |
|
| Trade overall |
|
Differences in the trade between India with China and the US
- The biggest difference in India’s trade with the US and China is that while it has a trade surplus with the US (USD 32.85 billion in 2021–2022), it has the largest trade deficit with China (USD 73.31 billion in 2021–2022) of any nation.
- While India’s imports from China climbed from USD 2 billion to USD 94.57 billion between 2001-02 and 2021-2020, the country’s exports to China increased just marginally, from roughly USD 1 billion to USD 21 billion.
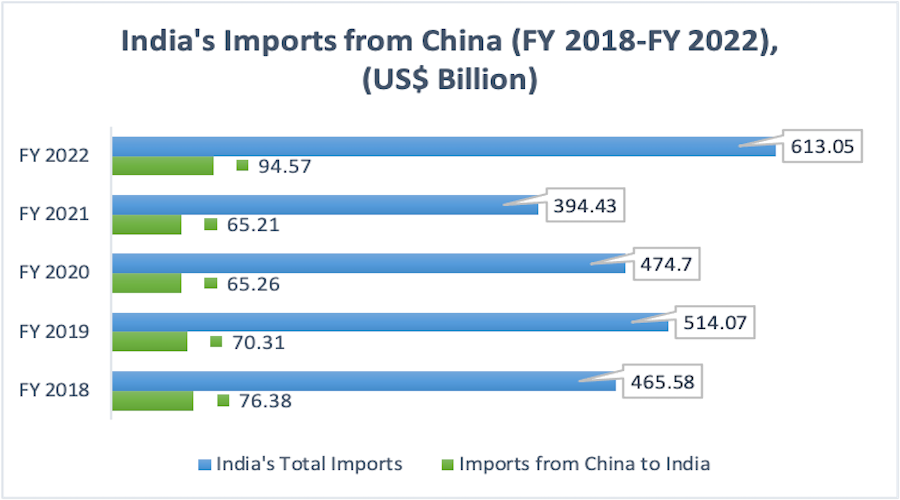
India China trade
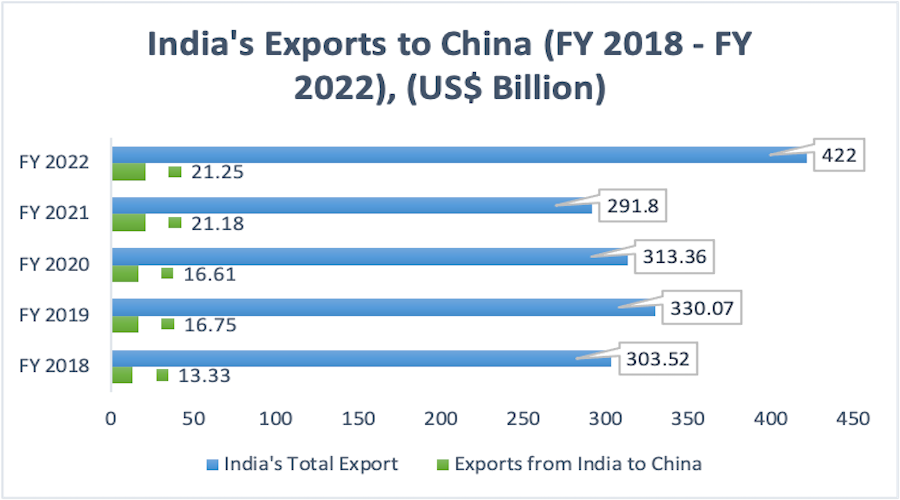
Exports to China
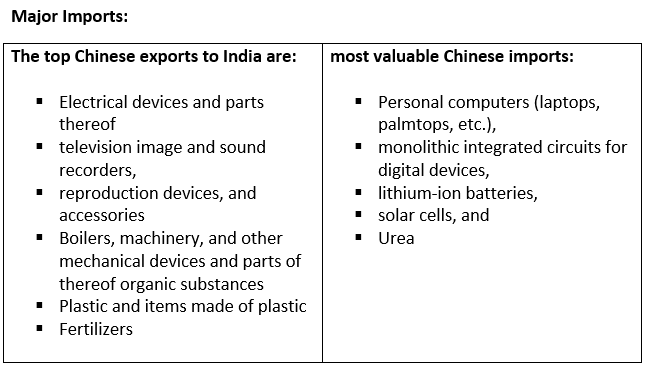
Major exports
India exported 5% of its total shipments to China in 2021–2022.
Among the biggest exports were :
- Ores, slag, and ash.
- Mineral fuels/oils and their distillation byproducts, bituminous compounds, and mineral waxes;
- steel and iron
- Articles of aluminum
- Cotton
- Light Naphtha was India’s most valuable export among individual goods.
China’s Heavy Import Dependence Imply
- The state’s difficulties in terms of politics and security are exacerbated, in the eyes of the administration, by its reliance on importing goods from hostile nations.
- The majority of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) used in India are imported. The majority of the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) used by India’s pharmaceutical sector are imported from China. Chinese APIs are less expensive than Indian ones, even in the Indian market.
- When supplies of Chinese APIs to India were temporarily halted due to travel restrictions during the Covid-19 outbreak, India had to reduce its exports of APIs as a result, exposing the extent of the issue.
- 24% of the coal energy produced in India may come from facilities that use essential Chinese imports. So while this might not be a clear-cut case of strategic reliance, it is unquestionably a security challenge.
- Although there are calls to restrict or even ban such imports from China, doing so would just result in the private Indian power companies having to bear greater expenses.
What has India done to combat China’s over-reliance?
- Chinese apps are prohibited
- Considering Chinese investments carefully and excluding Chinese companies from 5G testing
- Limiting opportunistic acquisition of domestic companies: FDI limit on China
- Promoting bulk drug parks and the PLI Scheme will reduce API import needs.
- Chinese power equipment imports are effectively prohibited
- Anti-dumping taxes were imposed on some chemicals and aluminum products for a period of five years to protect domestic manufacturers.
- Identification of 12 industries that can help India become a global supplier and reduce import costs:
Food processing, organic farming, iron, aluminum, copper, agrochemicals, electronics, industrial machinery, furniture, leather goods, shoes, auto components, textiles, as well as coveralls, masks, sanitizers, and ventilators, are some of these industries.
Current Accounts Deficit (CAD)
It is the difference between the amount of money coming in via exports and the amount leaving the country through imports. It calculates the difference between the amount of money coming into and leaving the country through the exchange of products and services, as well as the movement of funds from domestically owned manufacturing equipment to foreign countries.
Different from the trade balance
- It differs slightly from the Balance of Trade, which simply calculates the difference between income and expenses for exports and imports of goods and services.
- While the current account also takes payments from local capital sent abroad into account.
- For instance, the current account would be used to calculate the rental income from an Indian’s home in the UK, but not in the balance of trade.
Reasons
- Exchange rate in effect, amount of consumer spending, capital inflow, inflation level, and current interest rate.
- Imports of crude oil and gold are the main causes of India’s huge current account deficit.
Implications
- Depending on why an economy is running a deficit, the current account deficit may be a positive or bad indicator for that country.
- In the short run, it might be beneficial for a debtor country, but in the long run, it might cause investors to worry about getting a sufficient return on their investments.
Way ahead of India-China Trade
- By increasing exports and reducing imports of non-essential goods like electronics, gold, and mobile phones, it might be decreased.
- It would also be helpful to make it simpler for manufacturing companies to raise overseas capital and hedge their currency exposure.
- Among other things, the government and RBI may look into reviewing the FPI debt investment limits.
- India still has to import the majority of its essential goods to maintain its strategic competitiveness. It may, however, diversify this dependence by minimizing China’s contribution to it.
- By collaborating more with the United States, Europe, South Korea, and Japan, India can diversify its reliance. It will become more dependent on nations with whom it already has cordial political ties as a result.
- A wise course of action is to further encourage self-reliance in key areas where India is a net importer, and where technology and money will play a significant role.
Source:
Download the PDF now:
Plutus IAS Current Affairs eng med 16th Jan 2023
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Collect the best daily current affairs for the UPSC examination from Plutus IAS today free of cost. It is important for every UPSC examinee to read daily current affairs for the UPSC examination for their UPSC examination. Also read the Weekly, Monthly, and Yearly Current Affairs for IAS exam preparation.



No Comments